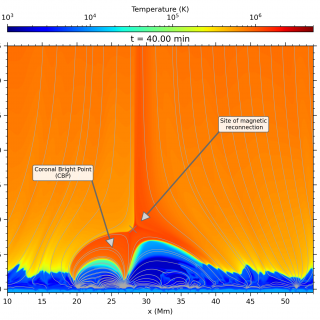
When the Sun is observed in X-ray or extreme ultraviolet wavelengths, hundreds of bright and compact structures with a rounded shape and sizes similar to that of our planet Earth can be easily distinguished in the solar corona. These structures are known as Coronal Bright Points or CBPs and they consist of sets of magnetic loops that connect areas of opposite magnetic polarity on the solar surface. These loops confine the solar plasma and in them, by mechanisms that have been debated for many years among solar physicists, the gas remains with temperatures of several million degrees, emitting
Advertised on