It may interest you
-
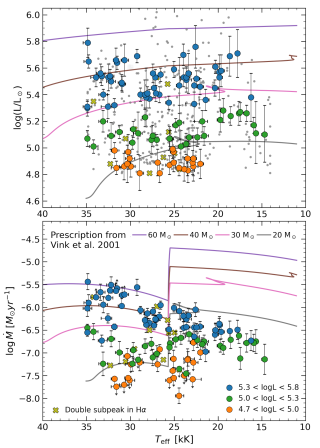 The properties of blue supergiants are key for constraining the end of the main sequence phase, a phase during which massive stars spend most of their lifetimes. The lack of fast-rotating stars below 21.000K, a temperature around which stellar winds change in behaviour, has been proposed to be caused by enhanced mass-loss rates, which would spin down the star. Alternatively, the lack of fast-rotating stars may be the result of stars reaching the end of the main sequence. Here, we combine newly derived estimates of photospheric and wind parameters, wind terminal velocities from the literatureAdvertised on
The properties of blue supergiants are key for constraining the end of the main sequence phase, a phase during which massive stars spend most of their lifetimes. The lack of fast-rotating stars below 21.000K, a temperature around which stellar winds change in behaviour, has been proposed to be caused by enhanced mass-loss rates, which would spin down the star. Alternatively, the lack of fast-rotating stars may be the result of stars reaching the end of the main sequence. Here, we combine newly derived estimates of photospheric and wind parameters, wind terminal velocities from the literatureAdvertised on -
 This educational programme, organised and developed by the scientific institutions of the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory and the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC), is celebrating its 14th birthday, and it does so with unanmiously high opinions from the schools which have participated in the programme this year. This can be gleaned from the data in the questionnaire circulated by the IAC among the educational centres which participated in this edition of the programme in 2024, which reflect 100% satisfaction. In 2024 the programme included 14 lectures in educational centres, andAdvertised on
This educational programme, organised and developed by the scientific institutions of the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory and the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC), is celebrating its 14th birthday, and it does so with unanmiously high opinions from the schools which have participated in the programme this year. This can be gleaned from the data in the questionnaire circulated by the IAC among the educational centres which participated in this edition of the programme in 2024, which reflect 100% satisfaction. In 2024 the programme included 14 lectures in educational centres, andAdvertised on -
 An international study led by Almudena Prieto, a researcher at the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) has found places where new stars are forming, as faint star clusters, around the centre of an evolved galaxy. This is the first time that young populations of stars have been picked out and dated in this type of galaxies dominated by very old stars, which can be called “rejuvenated old galaxies”. The research has combined observations from various telescopes, both ground based and space based, and has used innovative techniques of data analysis. The results are published in theAdvertised on
An international study led by Almudena Prieto, a researcher at the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) has found places where new stars are forming, as faint star clusters, around the centre of an evolved galaxy. This is the first time that young populations of stars have been picked out and dated in this type of galaxies dominated by very old stars, which can be called “rejuvenated old galaxies”. The research has combined observations from various telescopes, both ground based and space based, and has used innovative techniques of data analysis. The results are published in theAdvertised on