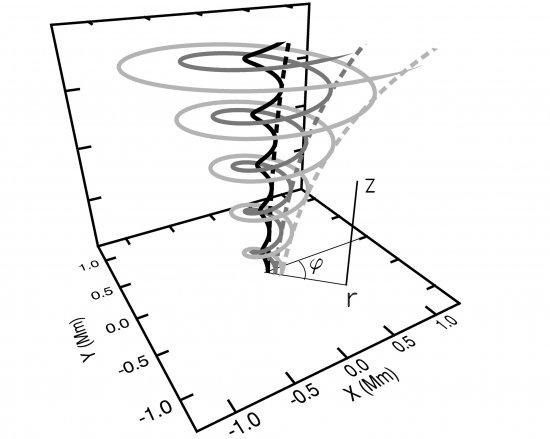
Recent high-resolution and high-cadence observations have surprisingly suggested that prominence barbs exhibit apparent rotating motions suggestive of a tornado-like structure. Additional evidence has been provided by Doppler measurements. The observations reveal opposite velocities for both hot and cool plasma on the two sides of a prominence barb. This motion is persistent for several hours and has been interpreted in terms of rotational motion of prominence feet. Several authors suggest that such barb motions are rotating helical structures around a vertical axis similar to tornadoes on Earth. One of the difficulties of such a proposal is how to support cool prominence plasma in almost-vertical structures against gravity. In this work we model analytically a tornado-like structure and try to determine possible mechanisms to support the prominence plasma. We have found that the Lorentz force can indeed support the barb plasma provided the magnetic structure is sufficiently twisted and/or significant poloidal flows are present.
Schematic picture of a tornado-like magnetic structure. Solid lines are the three-dimensional representation of the magnetic field lines. Dashed lines are thepoloidal field lines in the azimuthal plane.
Advertised on
References