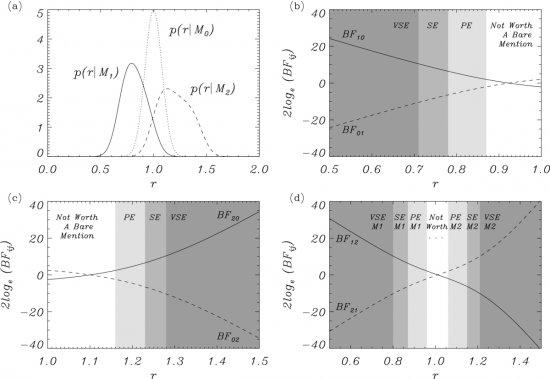
We present the first application of Bayesian model comparison techniques for solar atmospheric seismology. The detection of multiple mode harmonic kink oscillations in coronal loops enables to obtain information on coronal density stratification and magnetic field expansion using seismology inversion techniques. The inference is based on the measurement of the period ratio between the fundamental mode and the first overtone and theoretical results for the period ratio under the hypotheses of coronal density stratification and magnetic field expansion of the wave guide. We present a Bayesian analysis of multiple mode harmonic oscillations for the inversion of the density scale height and magnetic flux tube expansion, under each of the hypotheses. Then, the two models are compared using a Bayesian model comparison scheme to assess how plausible each one is, given our current state of knowledge
This figure displays the results from the Bayesian comparison for coronal loop models as: M0: uniform flux tubes; M1: density stratified flux tubes; M2: expanding magnetic flux tubes. (a) Marginal likelihood as a function of the observed period ratio, r,
Advertised on
References
2013, The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 765, L23