We present observations of the molecular gas in the nuclear environment of three prototypical low luminosity AGN (LLAGN), based on VLT/SINFONI AO-assisted integral-field spectroscopy of H2 1-0 S(1) emission at angular resolutions of ~0.17”. On scales of 50-150 pc the spatial distribution and kinematics of the molecular gas are consistent with a rotating thin disk, where the ratio of rotation (V) to dispersion (σ) exceeds unity. However, in the central 50 pc, the observations reveal a geometrically and optically thick structure of molecular gas (V/ σ < 1 and NH> 1023 cm-2) that is likely to be associated with the outer extentof any smaller scale obscuring structure. In contrast to Seyfert galaxies, the molecular gas in LLAGN has a V/ σ < 1 over an area that is ~9 times smaller and column densities that are in average ~3 times smaller. We interpret these results as evidence for a gradual disappearance of the nuclear obscuring structure. While a disk wind may not be able to maintain a thick rotating structure at these luminosities, inflow of material into the nuclear region could provide sufficient energy to sustain it. In this context, LLAGN may represent the final phase of accretion in current theories of torus evolution. While the inflow rate is significant during the Seyfert phase, it is slowly decreasing, and the collisional disk is gradually transitioning to become geometrically thin. Furthermore, the nuclear region of these LLAGN is dominated by intermediate-age/old stellar populations (with little or no on-going star formation), consistent with a late stage of evolution.
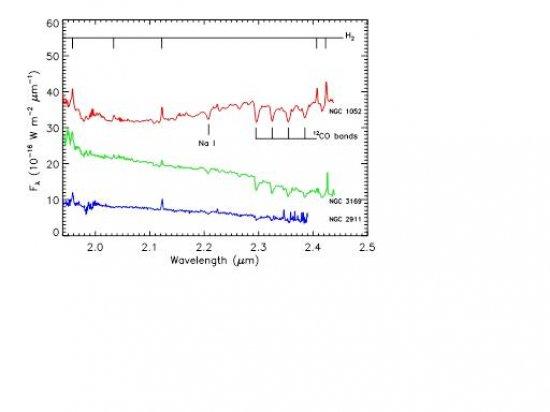
K-band nuclear spectra of LLAGN extracted from our SINFONI data in r = 0.3” apertures. The prominent emission lines are from H2 (marked at the top of the figure), the strongest being 1-0 S(1) at 2.12 μm. Several stellar absorption features (like the 12CO
Advertised on
References
IN PRESS