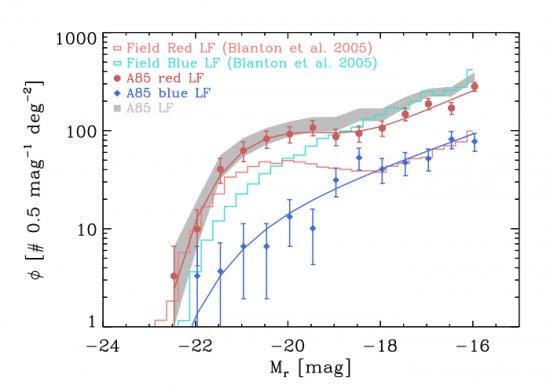
We present a new deep determination of the spectroscopic LF within the virial radius of the nearby and massive Abell 85 (A85) cluster down to the dwarf regime (M*+6) using VLT/VIMOS spectra for ~2000 galaxies with mr ≤ 21 mag and <μe,r > ≤ 24 mag arcsec-2. The resulting LF from 438 cluster members is best modeled by a double Schechter function due to the presence of a statistically significant upturn at the faint-end. The amplitude of this upturn (αf = -1.58+0.19-0.15), however, is much smaller than that of the SDSS composite photometric cluster LF by Popesso et al. (2006, αf ~-2). The faint-end slope of the LF in A85 is consistent, within the uncertainties, with that of the field. The red galaxy population dominates the LF at low luminosities, and is the main responsible for the upturn. The fact that the slopes of the spectroscopic LFs in the field and in a cluster as massive as A85 are similar suggests that the cluster environment does not play a major role in determining the abundance of low-mass galaxies. At the same time, it is important because it changes the nature of the dwarf galaxies transforming blue ones in field into red ones in high density regions as can be observe comparing the LFs of these populations.
Caption of the figure: The spectroscopic LF of A85 (gray shadow), blue and red diamonds show the LF of blue and red galaxies of A85. The full lines correspond to the Schecter function fits. The histograms are the LF of field red and blue galaxies (Blanton
Advertised on
References