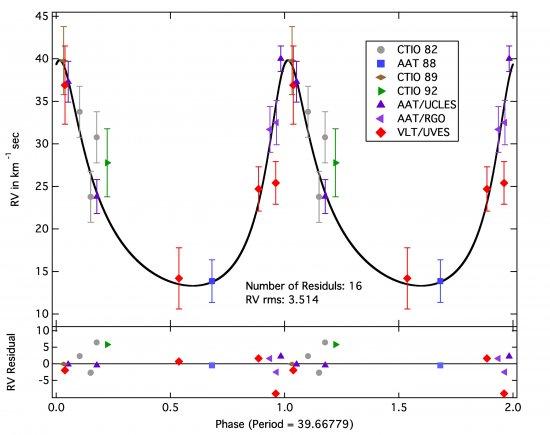
The stellar origin of the extremely hydrogen-deficient R Coronae Borealis (RCB) stars has remained a mystery for astronomers since their discovery more than two hundred years ago. Two competing scenarios are commonly advocated. In the first one, a final helium shell flash occurs on a cooling white dwarf star or a very late thermal pulse is experienced by a post-AGB star. The second scenario involves the merger of two white dwarfs: a carbon–oxygen white dwarf accretes ahelium white dwarf. Evidence from the chemical compositions of RCB stars suggests that most are products of a merger. However, no RCB star is known to be in a binary system. Here we report that the remarkable hot RCB star DY Cen is revealed to be the first and only binary system to be found among the RCB stars and their likely relatives, including the extreme helium stars and the hydrogen-deficient carbon stars. Radial velocity determinations from 1982 to 2010 have shown that DY Cen is a single-lined spectroscopic binary in an eccentric orbit with a period of 39.67 days. It is also one of the hottest and most H-rich member of the class of RCB stars. The system may have evolved from a common envelope to its current form. If DY Cen continues to contract at the rate suggested by the measurements of effective temperature and gravity, it is possible that there is no known star in the Galaxy quite like it.
Stellar radial velocity curve for DY Cen. The deviations of observations to the computed fit for the best orbital parameters are shown in the bottom. The notation of the observations is shown in the inset.
Advertised on
References
The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 2012, 760, L3