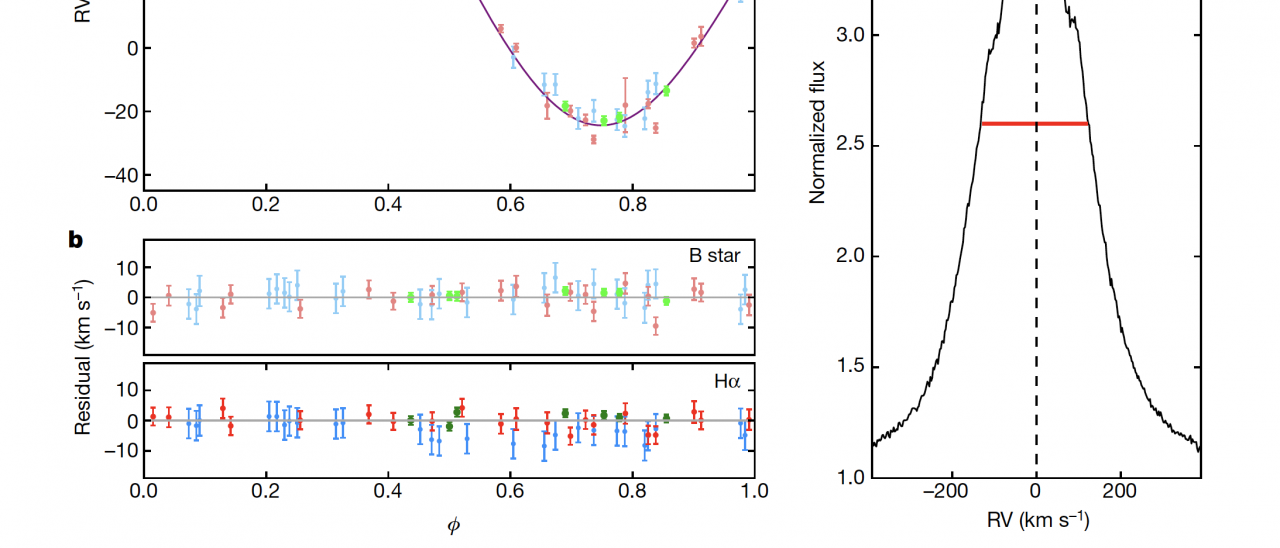
All stellar-mass black holes have hitherto been identified by X-rays emitted from gas that is accreting onto the black hole from a companion star. These systems are all binaries with a black-hole mass that is less than 30 times that of the Sun. Theory predicts, however, that X-ray-emitting systems form a minority of the total population of star–black-hole binaries. When the black hole is not accreting gas, it can be found through radial-velocity measurements of the motion of the companion star. We report here radial-velocity measurements taken over two years of the Galactic B-type star, LB-1. The star was initially discovered during a monitoring campaign with the 4-m telescope LAMOST and subsequently studied in more detail with the 10-m class telescopes GTC and Keck. We find that the motion of the B star and a superimposed Hα emission line (see figure) require the presence of a dark companion with a mass of 68 solar masses, which can only be a black hole. The long orbital period of 78.9 days shows that this is a wide binary system. For comparison, black holes detected in X-ray binaries have masses in the range 5-15 solar masses. On the other hand, gravitational-wave experiments have detected black holes with several tens of solar masses. However, the formation of a ~70 solar mass black hole in a high-metallicity environment is extremely challenging within current stellar evolution theories. This would require a significant reduction in wind mass-loss rates and overcoming the pair-instability supernova phase, which limits the maximum black hole mass to less than ~50 solar masses. Alternatively, the black hole in LB-1 might have formed after a binary black hole merger or other exotic mechanisms.
a) radial velocity curves and orbital fits for the B-star (purple) and its dark companion (orange), the latter extracted from the wings of the Hα emission (panel c). b) Residuals obtained after subtracting the best orbital models from the velocity points.
It may interest you
-
 The European Southern Observatory (ESO) has signed an agreement with an international consortium of institutions, including the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC), the Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía (IAA) and the Centro de Astrobiología de Madrid (CSIC-INTA), for the design and construction of ANDES, the ArmazoNes high Dispersion Echelle Spectrograph. The instrument will be installed on ESO’s Extremely Large Telescope (ELT). It will be used to search for signs of life in exoplanets and look for the very first stars, as well as to test variations of the fundamental constants ofAdvertised on
The European Southern Observatory (ESO) has signed an agreement with an international consortium of institutions, including the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC), the Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía (IAA) and the Centro de Astrobiología de Madrid (CSIC-INTA), for the design and construction of ANDES, the ArmazoNes high Dispersion Echelle Spectrograph. The instrument will be installed on ESO’s Extremely Large Telescope (ELT). It will be used to search for signs of life in exoplanets and look for the very first stars, as well as to test variations of the fundamental constants ofAdvertised on -
 The Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) organised the international conference From Fake News to Real Clusters: The Controversial Fate of High-z Galaxy Protoclusters, which was held at the IACTEC building of the Las Mantecas Technology Park in La Laguna (Tenerife, Spain) from 13 to 16 May 2025. This meeting brought together around 30 researchers dedicated to the study of protoclusters and large-scale structures in the early stages of the universe. The event focused on the latest findings from multi-frequency observations and advanced modelling techniques, with a special focus onAdvertised on
The Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) organised the international conference From Fake News to Real Clusters: The Controversial Fate of High-z Galaxy Protoclusters, which was held at the IACTEC building of the Las Mantecas Technology Park in La Laguna (Tenerife, Spain) from 13 to 16 May 2025. This meeting brought together around 30 researchers dedicated to the study of protoclusters and large-scale structures in the early stages of the universe. The event focused on the latest findings from multi-frequency observations and advanced modelling techniques, with a special focus onAdvertised on -
 The Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) is hosting the second Solar MHD ( UKUS 7) conference this week. Following the successful first edition held in Eastbourne (UK) in 2022, this event brings together nearly fifty international experts to discuss the latest advancements in solar magnetohydrodynamics. Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) is a branch of physics that studies the behavior of electrically conducting fluids, such as solar plasma. Understanding MHD processes in the Sun is essential for predicting phenomena like solar flares and coronal mass ejections, which can significantly impactAdvertised on
The Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) is hosting the second Solar MHD ( UKUS 7) conference this week. Following the successful first edition held in Eastbourne (UK) in 2022, this event brings together nearly fifty international experts to discuss the latest advancements in solar magnetohydrodynamics. Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) is a branch of physics that studies the behavior of electrically conducting fluids, such as solar plasma. Understanding MHD processes in the Sun is essential for predicting phenomena like solar flares and coronal mass ejections, which can significantly impactAdvertised on