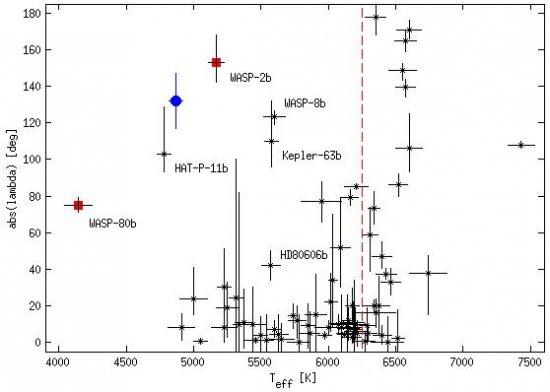
The measurement of the Rossiter-McLaughlin effect for transiting exoplanetsplaces constraints on the orientation of the orbital axis with respect to the stellar spin axis, which can shed light on the mechanisms shaping the orbital configuration of planetary systems. Here we present the interesting case of the Saturn-mass planet HAT-P-18b, which orbits one of the coolest stars for which the Rossiter-McLaughlin effect has been measured so far. We acquired a spectroscopic time-series, spanning a full transit, with the HARPS-N spectrograph mounted at the TNG telescope. The very precise radial velocity measurements delivered by the HARPS-N pipeline were used to measure the Rossiter-McLaughlin effect. Complementary new photometric observations of another full transit were also analysed to obtain an independent determination of the star and planet parameters. We find that HAT-P18b lies on a counter-rotating orbit, the sky-projected angle between the stellar spin axis and the planet orbital axis being λ=132 ± 15 deg. By joint modelling of the radial velocity and photometric data we obtain new determinations of the star (M* = 0.770 ± 0.027 MSun; R* = 0.717 ± 0.026 RSun; Vsin(I*) = 1.58 ± 0.18 km s-1) and planet (Mp = 0.196 ± 0.008 MJ ; Rp = 0.947 ± 0.044 RJ) parameters. Ourspectra provide for the host star an effective temperature Teff = 4870 ± 50 K, a surface gravity of log g* = 4.57± 0.07 cm s-2 , and an iron abundance of [Fe/H] = 0.10 ± 0.06. HAT-P-18b is one of the few planets known to transit a star with Teff <6250 K on a retrograde orbit. Objects such as HAT-P-18b (low planet mass and/orrelatively long orbital period) most likely have a weak tidal coupling with their parent stars, therefore their orbits preserve any original misalignment. As such, they are ideal targets to study the causes of orbital evolution in cool main-sequence stars.}
Caption: Compilation of the values of λ, measured via the RM effect, as a function of the host star effective temperature (see: http://www.astro.keele.ac.uk/jkt/tepcat/rossiter.html).HAT-P-18b is shown as a filled blue dot. For the two objects marked with
Advertised on
References