Simulations have shown that a diverse range of extrasolar terrestrial planet bulk compositions are likely to exist based on the observed variations in host star elemental abundances. Based on recent studies, it is expected that a significant proportion of host stars may have Mg/Si ratios below 1. Here we examine this previously neglected group of systems. Planets simulated as forming within these systems are found to be Mg-depleted (compared to Earth), consisting of silicate species such as pyroxene and various feldspars. Planetary carbon abundances also vary in accordance with the host star C/O ratio. The predicted abundances are in keeping with observations of polluted white dwarfs, lending validity to this approach. Further studies are required to determine the full planetary impacts of the bulk compositions predicted here.
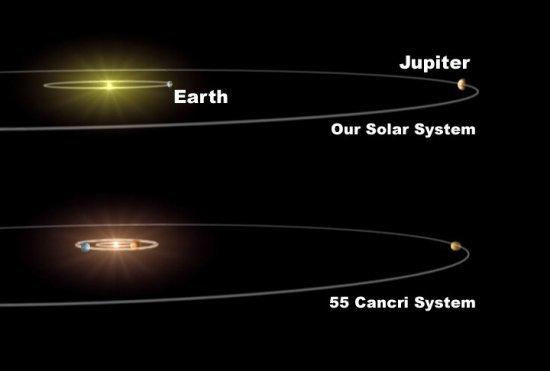
In this work, the planetary system of the planet-host star 55Cnc has been studied. In this system, there is an Earth-like planet that shows a chemical composition very different from that of the Earth.
Advertised on
References