It may interest you
-
 The Solar System research group at the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) is participating in the international programme to keep a closet track of asteroid 2024 YR4. The aim is to determine its orbit with the highest possible precision before it stops being observable by ground based and satellite telescopes in April, and so improving our value of the probability that it will impact the Earth in 2032. In this context several telescopes of the Canary Observatories of the IAC are playing an outstanding role in this observing campaign: The Gran Telescopio Canarias (GTC) at the Roque deAdvertised on
The Solar System research group at the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) is participating in the international programme to keep a closet track of asteroid 2024 YR4. The aim is to determine its orbit with the highest possible precision before it stops being observable by ground based and satellite telescopes in April, and so improving our value of the probability that it will impact the Earth in 2032. In this context several telescopes of the Canary Observatories of the IAC are playing an outstanding role in this observing campaign: The Gran Telescopio Canarias (GTC) at the Roque deAdvertised on -
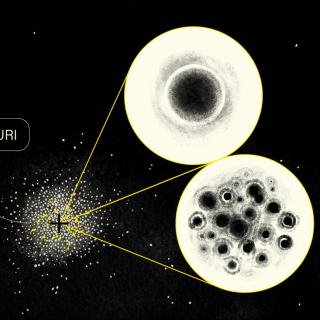 Omega Centauri is a large globular cluster, containing almost ten million stars, in the direction of the constellation of Centaurus, which has been studied to understand its stellar kinematics, the motions of its stars under the action of the gravitational forces which act on them. A research team at the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) has just published a study which shows that a group of black holes dominates the movements of its stellar kinematics. This result can be extended to certain other structures in the universe and goes against some previous claims about the role of lowAdvertised on
Omega Centauri is a large globular cluster, containing almost ten million stars, in the direction of the constellation of Centaurus, which has been studied to understand its stellar kinematics, the motions of its stars under the action of the gravitational forces which act on them. A research team at the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) has just published a study which shows that a group of black holes dominates the movements of its stellar kinematics. This result can be extended to certain other structures in the universe and goes against some previous claims about the role of lowAdvertised on -
 An international team, led by a researcher from the University of Liège (Belgium) affiliated to the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC), has discovered an extraordinarily light planet orbiting a distant star in our galaxy. This discovery, reported today in the journal Nature Astronomy, is a promising key to solving the mystery of how such giant, super-light planets form. The new planet, named WASP-193b, appears to dwarf Jupiter in size, yet it is a fraction of its density. The scientists found that the gas giant is 50 percent bigger than Jupiter, and about a tenth as dense — anAdvertised on
An international team, led by a researcher from the University of Liège (Belgium) affiliated to the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC), has discovered an extraordinarily light planet orbiting a distant star in our galaxy. This discovery, reported today in the journal Nature Astronomy, is a promising key to solving the mystery of how such giant, super-light planets form. The new planet, named WASP-193b, appears to dwarf Jupiter in size, yet it is a fraction of its density. The scientists found that the gas giant is 50 percent bigger than Jupiter, and about a tenth as dense — anAdvertised on
