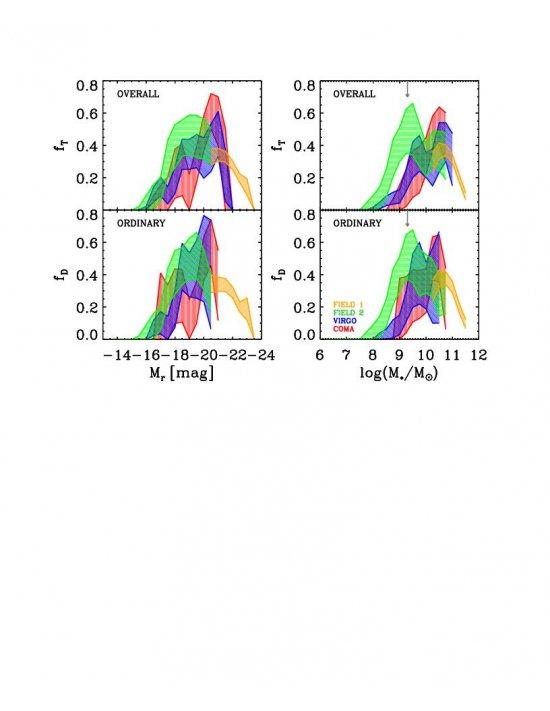
The effects that interactions produce on galaxy disks and how they modify the subsequent formation of bars need to be distinguished to fully understand the relationship between bars and environment. To this aim we derive the bar fraction in three different environments ranging from the field to Virgo and Coma Clusters, covering an unprecedentedly large range of galaxy luminosities (or, equivalently, stellar masses). We confirm that the fraction of barred galaxies strongly depends on galaxy luminosity. We also show that the difference between the bar fraction distributions as a function of galaxy luminosity (and mass) in the field and Coma Cluster is statistically significant, with Virgo being an intermediate case. The fraction of barred galaxies shows a maximum of about 50% at Mr~20.5 in clusters, whereas the peak is shifted to Mr~-19 in the field. We interpret this result as a variation of the effect of environment on bar formation depending on galaxy luminosity. We speculate that brighter disk galaxies are stable enough against interactions to keep their cold structure, thus, the interactions are able to trigger bar formation. For fainter galaxies, the interactions become strong enough to heat up the disks inhibiting bar formation and even destroying the disks. Finally, we point out that the controversy regarding whether the bar fraction depends on environment could be resolved by taking into account the different luminosity ranges probed by the galaxy samples studied so far.
Bar fraction distribution as function of the galaxy magnitudes (left panels) and masses (right panels). The bar fraction calculated using all the Hubble types (fT) and only the disk galaxies (fD) are plotted in the upper and bottom panels, respectively. T
Advertised on
References
2012ApJ, 761L, 6M