In order to fully understand the gravitational collapse of molecular clouds, the star formation process, and the evolution of circumstellar disks, these phenomena must be studied in different Galactic environments with a range of stellar contents and positions in the Galaxy. The young massive association Cygnus OB2, in the Cygnus-X region, is a unique target to study how star formation and the evolution of circumstellar disks proceed in the presence of a large number of massive stars. We present a catalog obtained with recent optical observations in the r, i, z filters with OSIRIS, mounted on the 10.4 m Gran Telescopio CANARIAS telescope, which is the deepest optical catalog of Cyg OB2 to date. The catalog consists of 64,157 sources down to M = 0.15 M ☉ at the adopted distance and age of Cyg OB2. A total of 38,300 sources have good photometry in all three bands. We combined the optical catalog with existing X-ray data of this region, in order to define the cluster locus in the optical diagrams. The cluster locus in the r – i versus i – z diagram is compatible with an extinction of the optically selected cluster members in the 2.64 m < AV < 5.57 m range. We derive an extinction map of the region, finding a median value of AV = 4.33 m in the center of the association, decreasing toward the northwest. In the color-magnitude diagrams, the shape of the distribution of main-sequence stars is compatible with the presence of an obscuring cloud in the foreground ~850 ± 25 pc from the Sun.
Advertised on
References
2012 ApJS, 202, 19
It may interest you
-
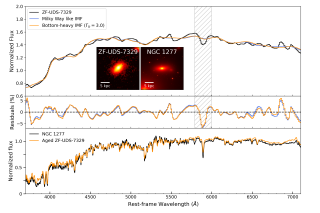 Observations made with the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) have revealed a larger-than-expected number of massive galaxies when the Universe was still young. The focus of this study is precisely one of these galaxies, ZF-UDS-7329. It is a very compact object, and its spectrum suggests that it formed at a very early stage, when the Universe was around 2 billion years old. According to theoretical predictions, these objects first formed a generation of stars at the center of their dark matter halos and subsequently grew by merging with other halos. However, due to the random nature of theseAdvertised on
Observations made with the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) have revealed a larger-than-expected number of massive galaxies when the Universe was still young. The focus of this study is precisely one of these galaxies, ZF-UDS-7329. It is a very compact object, and its spectrum suggests that it formed at a very early stage, when the Universe was around 2 billion years old. According to theoretical predictions, these objects first formed a generation of stars at the center of their dark matter halos and subsequently grew by merging with other halos. However, due to the random nature of theseAdvertised on -
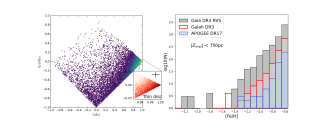 The formation and evolution of the disk of our Galaxy, the Milky Way, remains an enigma in astronomy. In particular, the relationship between the thick disk and the thin disk —two key components of the Milky Way— is still unclear. Understanding the chemical and dynamical properties of the stars within these disks is crucial, especially in the parameter spaces where their characteristics overlap, such the metallicity regime around [Fe/H] ~ -0.7, which marks the metal-poor end of the thin disk, higher than that of the thick disk. This is often interpreted as an indication that the thin diskAdvertised on
The formation and evolution of the disk of our Galaxy, the Milky Way, remains an enigma in astronomy. In particular, the relationship between the thick disk and the thin disk —two key components of the Milky Way— is still unclear. Understanding the chemical and dynamical properties of the stars within these disks is crucial, especially in the parameter spaces where their characteristics overlap, such the metallicity regime around [Fe/H] ~ -0.7, which marks the metal-poor end of the thin disk, higher than that of the thick disk. This is often interpreted as an indication that the thin diskAdvertised on -
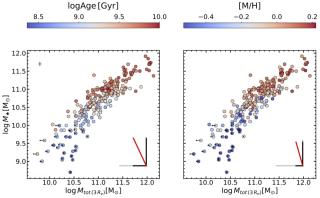 Despite the fundamental role that dark matter halos play in our theoretical understanding of galaxy formation and evolution, the interplay between galaxies and their host dark matter halos remains highly debated from an observational perspective. This lack of conclusive observational evidence ultimately arises from the inherent difficulty of reliably measuring dark matter (halo) properties. Based on detailed dynamical modeling of nearby galaxies, in this work we proposed a novel observational approach to quantify the potential effect that dark matter halos may have in modulating galaxyAdvertised on
Despite the fundamental role that dark matter halos play in our theoretical understanding of galaxy formation and evolution, the interplay between galaxies and their host dark matter halos remains highly debated from an observational perspective. This lack of conclusive observational evidence ultimately arises from the inherent difficulty of reliably measuring dark matter (halo) properties. Based on detailed dynamical modeling of nearby galaxies, in this work we proposed a novel observational approach to quantify the potential effect that dark matter halos may have in modulating galaxyAdvertised on
