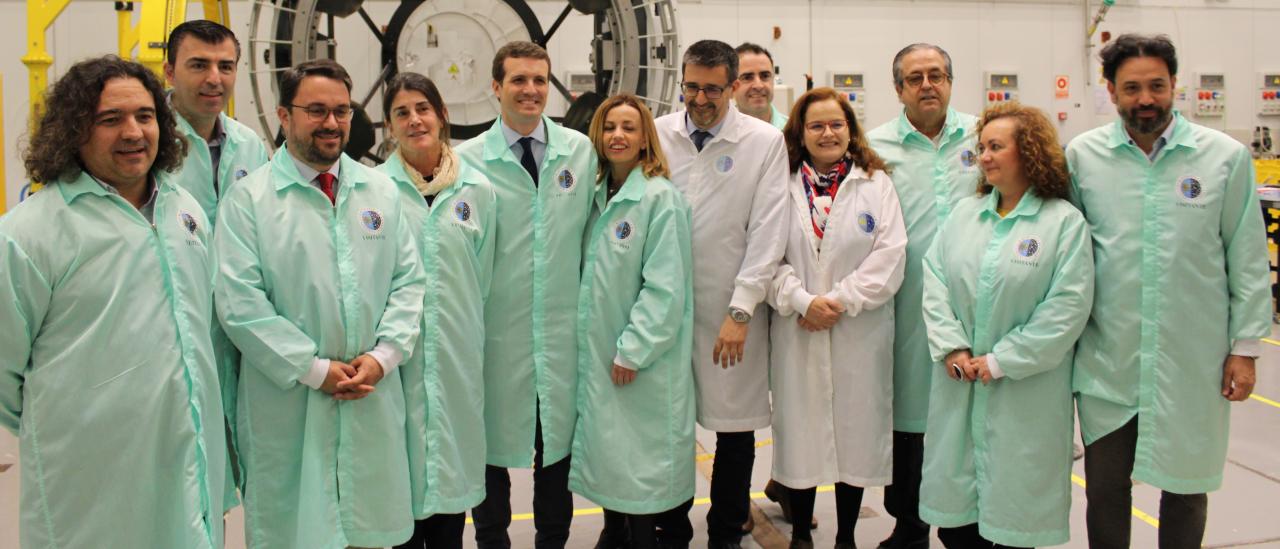
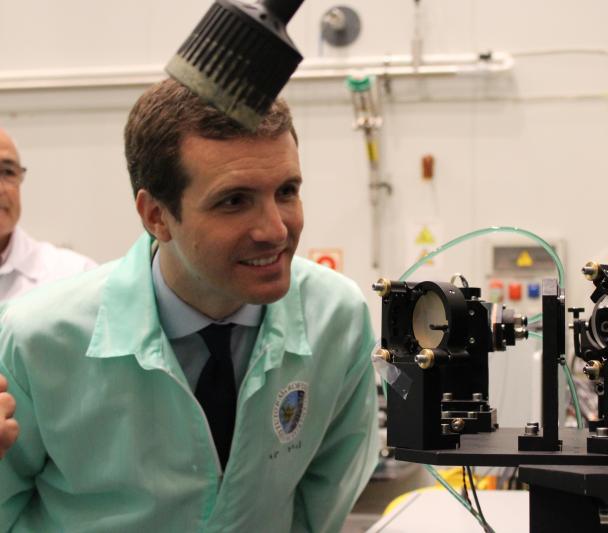
Esta mañana, Pablo Casado, presidente del Partido Popular (PP) y candidato a la Presidencia del Gobierno de España, visitó la sede central del Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC), en La Laguna, junto con otros representantes de su partido. El político se mostró interesado en conocer la labor investigadora y de desarrollo tecnológico que se realiza en el IAC y en los Observatorios de Canarias, así como los proyectos de futuros telescopios. Acompañado por Casiana Muñoz-Tuñón, subdirectora del IAC, y otros miembros del Comité de Dirección de este centro, Casado recorrió las instalaciones y accedió a los talleres y laboratorios donde se diseñan, fabrican y montan los instrumentos que después se envían tanto a telescopios terrestres como al espacio.
Pablo Casado junto a representantes de su partido y miembros del Comité de Dirección del Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias. Crédito: Jorge Dóniz (IAC).
Advertised on