The hypothesis of a universal initial mass function (IMF) - motivated by observations in nearby stellar systems - has been recently challenged by the discovery of a systematic variation of the IMF with the centralvelocity dispersion, σ, of early-type galaxies (ETGs), towards an excessof low-mass stars in high-σ galaxies. This trend has been derived so farfrom integrated spectra, and remains unexplained at present. To testwhether such trend depends on the local properties within a galaxy, we have obtained new, extremely deep, spectroscopic data, for three nearby ETGs, two galaxies with high σ (~300 km/s), and one lower mass system, with σ ~100 km/s. From the analysis of IMF-sensitive spectral features, we find that the IMF depends significantly ongalactocentric distance in the massive ETGs, with the enhanced fraction of low-mass stars mostly confined to their central regions. In contrast, the low-σ galaxy does not show any significant radial gradient in the IMF, well described by a shallower distribution, relative to the innermost regions of massive galaxies, at all radii. Such a result indicates that the IMF should be regarded as a local (rather than global) property, and suggests a significant difference between the formation process of the core and the outer regions ofmassive ETGs
Advertised on
References
It may interest you
-
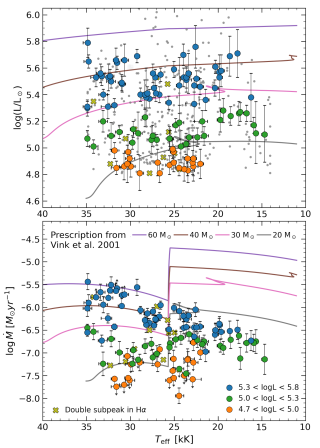 The properties of blue supergiants are key for constraining the end of the main sequence phase, a phase during which massive stars spend most of their lifetimes. The lack of fast-rotating stars below 21.000K, a temperature around which stellar winds change in behaviour, has been proposed to be caused by enhanced mass-loss rates, which would spin down the star. Alternatively, the lack of fast-rotating stars may be the result of stars reaching the end of the main sequence. Here, we combine newly derived estimates of photospheric and wind parameters, wind terminal velocities from the literatureAdvertised on
The properties of blue supergiants are key for constraining the end of the main sequence phase, a phase during which massive stars spend most of their lifetimes. The lack of fast-rotating stars below 21.000K, a temperature around which stellar winds change in behaviour, has been proposed to be caused by enhanced mass-loss rates, which would spin down the star. Alternatively, the lack of fast-rotating stars may be the result of stars reaching the end of the main sequence. Here, we combine newly derived estimates of photospheric and wind parameters, wind terminal velocities from the literatureAdvertised on -
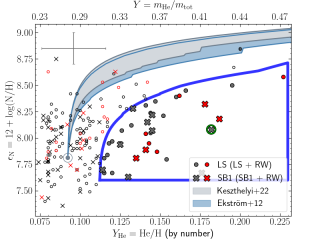 There is increasing evidence that single-star evolutionary models are unable to reproduce all of the observational properties of massive stars. Binary interaction has emerged as a key factor in the evolution of a significant fraction of massive stars. In this study, we investigate the helium (Y(He)) and nitrogen surface abundances in a comprehensive sample of 180 Galactic O-type stars with projected rotational velocities of ≤150 km/s. We found a subsample (~20% of the total, and ~80% of the stars with Y(He) ≥ 0.12) with a Y(He) and nitrogen abundance combined pattern that is unexplainable byAdvertised on
There is increasing evidence that single-star evolutionary models are unable to reproduce all of the observational properties of massive stars. Binary interaction has emerged as a key factor in the evolution of a significant fraction of massive stars. In this study, we investigate the helium (Y(He)) and nitrogen surface abundances in a comprehensive sample of 180 Galactic O-type stars with projected rotational velocities of ≤150 km/s. We found a subsample (~20% of the total, and ~80% of the stars with Y(He) ≥ 0.12) with a Y(He) and nitrogen abundance combined pattern that is unexplainable byAdvertised on -
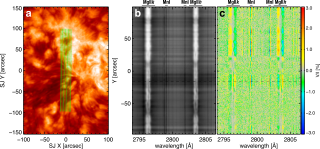 The magnetic field in the solar chromosphere plays a key role in the heating of the outer solar atmosphere and in the build-up and sudden release of energy in solar flares. However, uncovering the magnetic field vector in the solar chromosphere is a difficult task because the magnetic field leaves its fingerprints in the very faint polarization of the light, which is far from easy to measure and interpret. We analyse the spectropolarimetric observations obtained with the Chromospheric Layer Spectropolarimeter on board a sounding rocket. This suborbital space experiment observed the nearAdvertised on
The magnetic field in the solar chromosphere plays a key role in the heating of the outer solar atmosphere and in the build-up and sudden release of energy in solar flares. However, uncovering the magnetic field vector in the solar chromosphere is a difficult task because the magnetic field leaves its fingerprints in the very faint polarization of the light, which is far from easy to measure and interpret. We analyse the spectropolarimetric observations obtained with the Chromospheric Layer Spectropolarimeter on board a sounding rocket. This suborbital space experiment observed the nearAdvertised on