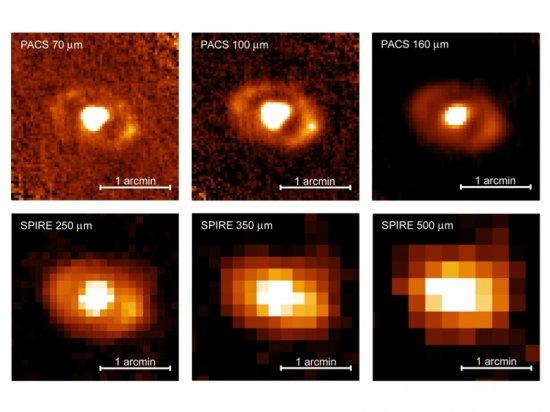
We report far-infrared (FIR) imaging of the Seyfert 2 galaxy NGC 3081 in the range 70- 500 μm, obtained with an unprecedented angular resolution, using the Herschel Space Observatory instruments PACS and SPIRE. The 11 kpc (∼70′′) diameter star-forming ring of the galaxy appears resolved up to 250 μm. We extracted infrared (1.6-500 μm) nuclear fluxes, that is active nucleus-dominated fluxes, and fitted them with clumpy torus models, which successfully reproduce the FIR emission with small torus sizes. Adding the FIR data to the near- and mid-infrared spectral energy distribution (SED) results in a torus radial extent of Ro=4±2 pc, as well as in a flat radial distribution of the clouds (i.e. the q parameter). At wavelengths beyond 200 μm, cold dust emission at T=28±1 K from the circumnuclear star-forming ring of 2.3 kpc (∼15′′) in diameter starts making a contribution to the nuclear emission. The dust in the outer parts of the galaxy is heated by the interstellar radiation field (19±3 K).
Caption of the figure: Herschel PACS 70, 100, and 160 μm images (top) and SPIRE 250, 350, and 500 μm maps (bottom). North is up and East is to the left. The 11 kpc diameter ring is resolved up to 250 μm.
Advertised on