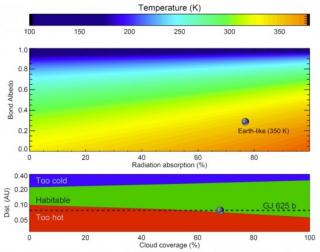
We report the discovery of a new super-Earth orbiting the nearby cool dwarf star GJ 625 in the inner edge of the habitable zone. This result has been achieved thanks to the analysis of the radial velocity (RV) time series from the HARPS-N spectrograph, in particular, 151 HARPS-N measurements taken over 3.5 yr. The planet GJ 625 b has a mass of roughly 2.8 Earth masses and an orbital period of ~14.6 days at a distance of ~0.08 AU of its host star. The star GJ 625 is a low-activity M dwarf star located at 6.5 pc (~21 light years) from the Sun, with a stellar rotation period in the range 75-85
Advertised on