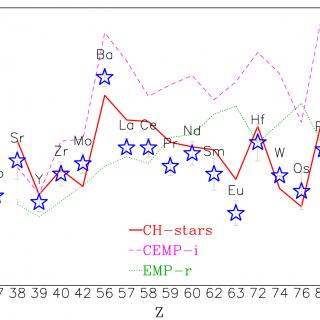
and CO(7-6) ALMA maps of the narrow (broad) emission HST imaging and narrow and broad components ALMA maps of ID2299. The top-left panel shows the HST-F814W imaging of the source, sampling the UV rest-frame emission from young stars. The top (bottom) rows show the CO(2-1), CO(5-4), [CI](2-1) and CO(7-6) ALMA maps of the narrow (broad) emission](/sites/default/files/styles/crop_square_2_2_to_320px/public/images/news/nature_210111.png?h=3df1cc9d&itok=uyk1HUVd)
An international study published in Nature Astronomy, in which the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) is a participant, suggests that the feedback winds do not have a direct impact on braking the formation of stars in massive galaxies, and attributes the process to other events such as ejection by huge tides caused when galaxies merge.
Advertised on