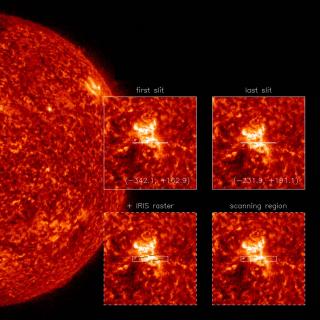
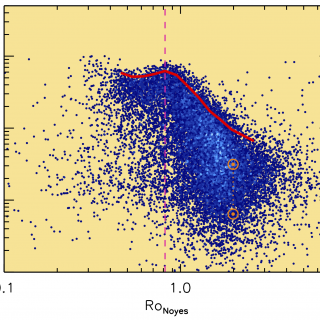
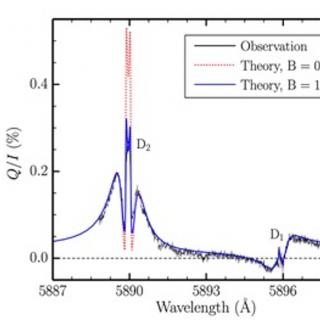
One of the most interesting questions for astrophysicists for the past few decades is how and when did the first galaxies form. One of the possible answers to “how” is that star formation in the first galaxies took place at a steady rate, building up a system with increasing mass. Another possibility is that the formation was more violent and discontinuous, with intense bursts of star formation, on short timescales, triggered by events such as galaxy mergers and strong concentrations of gas.
Advertised on