General
The Sun is a magnetically active star with violent eruptions that can hit Earth´s magnetosphere and cause important perturbations in our technology-dependent society. The objective of the Whole Sun project is to tackle in a coherent way for the first time key questions in Solar Physics that involve as a whole the solar interior and the atmosphere. Our star, the Sun, is a magnetically active celestial body. Its atmosphere undergoes violent eruptions, which are difficult to predict. The largest eruptions, after traversing the interplanetary space, can hit and deform Earth´s magnetosphere and cause important perturbations in our technology-dependent society.
The intense research in solar astrophysics in the past decades has produced important advancement in the knowledge of the solar structure and dynamics. Yet, there remain fundamental questions without a fully satisfactory answer, like: which processes in the interior lead to the generation of the solar magnetic field and why does the Sun have a magnetic activity cycle? What exactly is the mechanism leading to the giant magnetic eruptions seen in its atmosphere? What is the mutual relationship between the interior and the atmosphere? The objective of The Whole Sun project is to tackle these key questions that concern simultaneously the interior and the atmosphere as a coherent whole for the first time.
Until now, the research on the Sun had been carried out through the separate study of its interior, the low atmosphere and the corona, without a global, integrated vision of the complex dynamics that links the plasma in those regions. To understand and provide quantitative explanations for the physical processes in them one has to use advanced concepts of fluid dynamics, electromagnetism, kinetic theory and, additionally for the atmosphere, radiation-matter interaction; one has to apply refined techniques of theoretical and numerical modeling using massively parallel supercomputing installations; one must also carry out and interpret observations acquired in the advanced telescope installations on the ground and in space available at present. The Whole Sun project brings together five European institutions with leading solar physics research groups; we want to attain a deeper understanding of our star by linking the physics of its interior and atmosphere. To achieve that goal, we have to overcome important hurdles like: simultaneous consideration of very different space and time scales; challenging coupling of microphysics effects next to continuum physics and global effects; bringing together and coupling computer codes that were created separately with a specific region in mind. Our goal is to tackle these problems through the development of deep theoretical understanding of our star and the construction of the most advanced solar code of multiple space and time resolution attainable at present.
Members
Results
Highlights
Solar atmosphere ejections
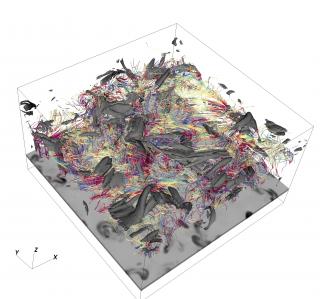
Many open questions remain regarding key ejection phenomena in the solar atmosphere, such as coronal jets, surges, and spicules. We have addressed various aspects of these events. For example, we have shown that the characteristics of observed surges and kernels (plasmoids) accompanying coronal jets—as well as the presence of double-chambered structures—closely resemble features predicted by numerical jet models (Joshi et al. 2020). We have also characterized, for the first time, the chromospheric and transition region properties of surges by combining high-resolution observations with advanced techniques such as k-means clustering, inversions, and density diagnostics (Nóbrega-Siverio et al. 2021). In addition, we have contributed to the understanding of coronal and transition region responses to recently reported chromospheric downflowing rapid redshifted excursions (RREs, Bose et al. 2021).
We have investigated the impact of coronal jets on prominences through both 2.5D numerical simulations (Luna & Moreno-Insertis, 2021) and multi-wavelength observations (Joshi et al. 2023), finding good agreement between theory and observation. Large-amplitude oscillations in prominences triggered by jets and flares have also been analyzed, revealing that hot plasma flows from flares can excite longitudinal filament oscillations via magnetic connectivity (Luna et al. 2024).
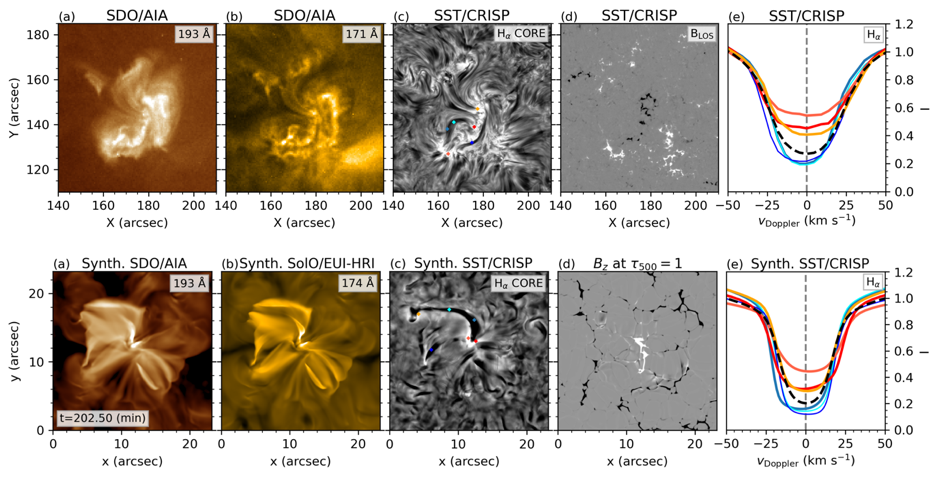
More recently, coordinated SST, IRIS, and SDO observations were used to study ephemeral magnetic flux emergence and the resulting chain of small-scale energetic events, demonstrating the importance of high-resolution magnetograms in unveiling the mechanisms behind EBs, UV bursts, and surges (Nóbrega-Siverio et al. 2024). Similar coordinated campaigns have helped uncover key properties of jets driven by magnetic reconnection in mixed-polarity regions. In these environments, evolving magnetic topologies—including flux ropes and null points—trigger both hot and cool jets that display widening, untwisting motions, and plasma fallback, with reconnection sites migrating along magnetic field lines. These dynamics appear to be characteristic of impulsive jets across diverse solar settings (Joshi et al. 2024a, 2024b).
Additionally, a data-constrained 3D MHD simulation based on a non-force-free field extrapolation has offered new insights into the onset and thermal evolution of coronal jets in active regions (Nayak et al. 2024).
Coronal Bright Points (CBPs)
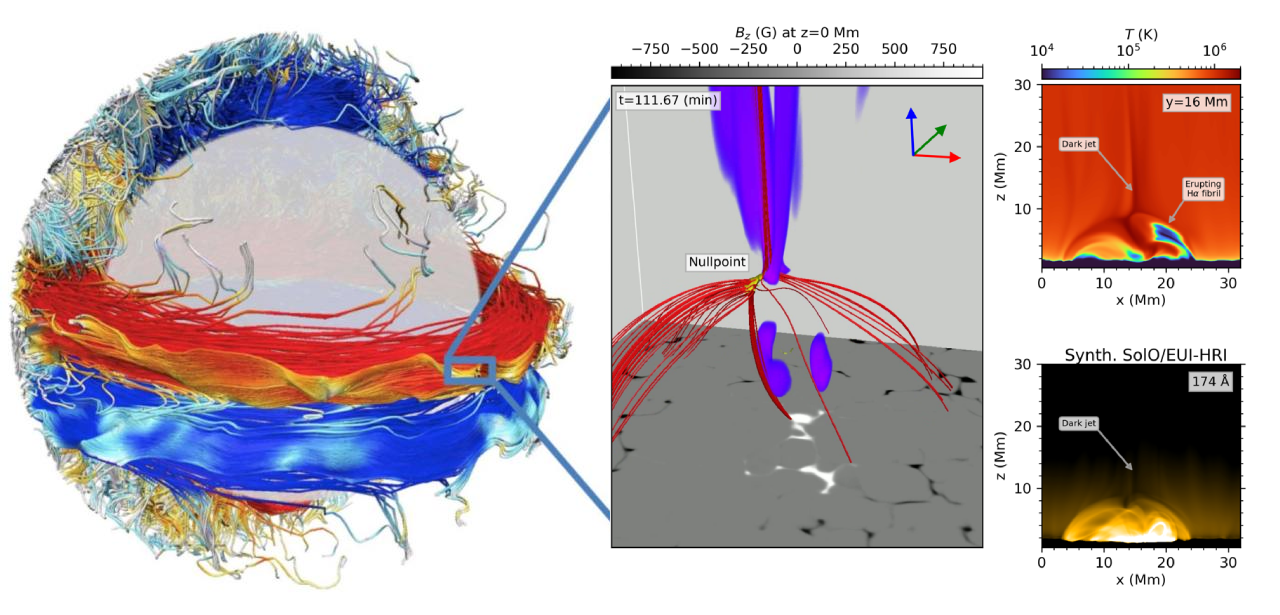
We have developed a comprehensive 3D radiative-MHD model of a CBP using the Bifrost code, based on a magnetic null point configuration—commonly associated with this type of phenomenon. Our results show that CBPs can be sustained for several hours through the continuous action of stochastic convective motions in the photosphere, without requiring large-scale or organized flows such as convergence. We also detect continuous upflows with faint EUV signatures, resembling dark coronal jets, as well as small-scale eruptions when chromospheric fibrils interact with the reconnection site (Nóbrega-Siverio et al. 2023).
We have further explored the chromospheric counterpart of CBPs using both observations and simulations, gaining deeper insight into plasma heating in small-scale loops and the chromosphere beneath CBPs (Madjarska et al. 2021, Bose et al. 2023, Nóbrega-Siverio and Moreno-Insertis 2022).
Nonequilibrium and partial ionization
We have studied the effects of nonequilibrium ionization and partial ionization on the dynamics and thermodynamics of magnetized plasma emerging from the solar interior through numerical experiments (Nóbrega-Siverio et al. 2020a). To this end, we implemented a new Fortran module in the Bifrost code to compute the ambipolar diffusion term in the Generalized Ohm’s Law efficiently (Nóbrega-Siverio et al. 2020b). More recently, we have analyzed this term from a mathematical standpoint, identifying new families of self-similar solutions that can serve as stringent tests for MHD codes including ambipolar diffusion—both in cylindrical coordinates (Moreno-Insertis et al. 2022) and in Cartesian ones (Moreno-Insertis et al., to be submitted).
Magnetic reconnection
We have implemented several resistivity models in the radiative-MHD Bifrost code to evaluate their impact on magnetic reconnection and determine which are better suited to reproduce solar features and inform diagnostics for current and upcoming space missions (Faerder et al. 2023, Faerder et al. 2024a, Faerder et al. 2024b).
High-resolution observations of fine-scale chromospheric blobs in flare ribbons provide evidence for fragmented reconnection in flare current sheets (Thoen Faber et al. 2025), while coupled tearing-thermal simulations reveal how condensations can form within flux ropes during the nonlinear stage of reconnection (De Jonghe & Sen 2025). Furthermore, we have studied the magnetic topologies linking Quiet-Sun Ellerman Bombs (QSEBs) and UV brightenings, identifying key 3D structures such as fan-spine configurations and magnetic null points as essential for understanding connectivity between the chromosphere and transition region (Bhatnagar et al. 2025).
Coronal rain
We have explored flare-driven coronal rain using resistive MHD simulations with the MPI-AMRVAC code, modeling the self-consistent formation and eruption of magnetic flux ropes via spontaneous reconnection across current sheets. In the post-eruption phase, thermal imbalance leads to catastrophic cooling and the formation of condensations that fall along field lines as coronal rain. The simulated dynamical and thermodynamic properties of these cool condensations show good agreement with observations of post-flare coronal rain (Sen et al. 2024).
Quiet Sun
We have conducted a statistical analysis of magnetic flux sheet emergence in the quiet Sun, demonstrating their contribution to the photospheric magnetic budget and their association with granular-scale processes, including exploding granules and granular lanes (Díaz-Castillo et al. 2025).
Polarization
We have investigated the role of angular and frequency coupling in modeling polarization in the Mg II h and k lines. Our results show when the angle-average approximation is valid and how angle-dependent effects can be efficiently incorporated into 1D radiative transfer modeling, particularly in the context of CLASP2-like observations (del Pino Alemán et al. 2025).
Solar satellites
We have contributed to the IRIS mission review (De Pontieu et al. 2021), highlighting how it has advanced our understanding of spicules, jets, and their formation.
In addition, we have collaborated on two studies related to the proposed Multi-slit Solar Explorer (MUSE) MIDEX mission, providing synthetic observables from realistic simulations to demonstrate the mission’s potential for solar diagnostics (De Pontieu et al. 2022, Cheung et al. 2022).
Scientific activity
Related publications
Related talks
No related talks were found.Related conferences
No related conferences were found.