Bibcode
Agarwal, N.; Ho, Shirley; Myers, Adam D.; Seo, Hee-Jong; Ross, Ashley J.; Bahcall, Neta; Brinkmann, Jonathan; Eisenstein, Daniel J.; Muna, Demitri; Palanque-Delabrouille, Nathalie; Pâris, Isabelle; Petitjean, Patrick; Schneider, Donald P.; Streblyanska, A.; Weaver, Benjamin A.; Yèche, Christophe
Bibliographical reference
Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics, Issue 04, article id. 007, pp. (2014).
Advertised on:
4
2014
Citations
21
Refereed citations
18
Description
Photometric large scale structure (LSS) surveys probe the largest
volumes in the Universe, but are inevitably limited by systematic
uncertainties. Imperfect photometric calibration leads to biases in our
measurements of the density fields of LSS tracers such as galaxies and
quasars, and as a result in cosmological parameter estimation. Earlier
studies have proposed using cross-correlations between different
redshift slices or cross-correlations between different surveys to
reduce the effects of such systematics. In this paper we develop a
method to characterize unknown systematics. We demonstrate that while we
do not have sufficient information to correct for unknown systematics in
the data, we can obtain an estimate of their magnitude. We define a
parameter to estimate contamination from unknown systematics using
cross-correlations between different redshift slices and propose
discarding bins in the angular power spectrum that lie outside a certain
contamination tolerance level. We show that this method improves
estimates of the bias using simulated data and further apply it to
photometric luminous red galaxies in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey as a
case study.
Related projects
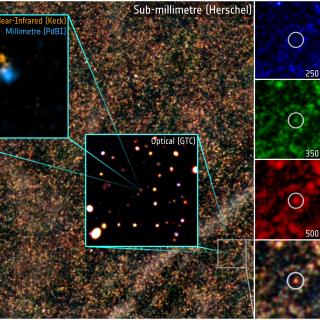
Formation and Evolution of Galaxies: Observations in Infrared and other Wavelengths
This IAC research group carries out several extragalactic projects in different spectral ranges, using space as well as ground-based telescopes, to study the cosmological evolution of galaxies and the origin of nuclear activity in active galaxies. The group is a member of the international consortium which built the SPIRE instrument for the
Ismael
Pérez Fournon
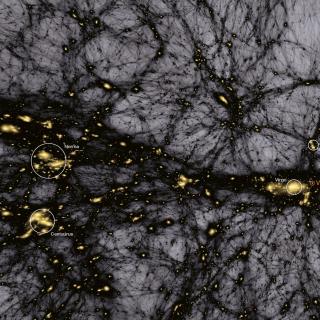
Cosmology with Large Scale Structure Probes
The Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) contains the statistical information about the early seeds of the structure formation in our Universe. Its natural counterpart in the local universe is the distribution of galaxies that arises as a result of gravitational growth of those primordial and small density fluctuations. The characterization of the
FRANCISCO SHU
KITAURA JOYANES