Bibcode
Alonso-Arias, P.; Cuttaia, F.; Terenzi, L.; Simonetto, A.; Fuerte-Rodríguez, P. A.; Hoyland, R.; Rubiño-Martín, J. A.
Bibliographical reference
Journal of Instrumentation
Advertised on:
2
2024
Citations
1
Refereed citations
0
Description
The Tenerife Microwave Spectrometer (TMS) is a ground-based radio-spectrometer that will take absolute measurements of the sky between 10–20 GHz. To ensure the sensitivity and immunity to systematic errors of these measurements, TMS includes an internal calibration system optimised for the TMS band, and cooled down to 4 K. It consists of an Aluminium core, composed of a baseplate and a bed of pyramidal elements coated with an absorber material and a metallic shield. The absorber coating is made of a commercial resin ECCOSORB CR/MF 117. To achieve the high stability (± 1 mK/h), temperature homogeneity (thermal gradients ΔT ≤ 25 mK), and emissivity (e ≥ 0.999) requirements of the reference unit, careful consideration has been given to the RF and thermal properties of the materials, as well as their geometry. In summary, this paper presents a comprehensive account of the design, characterisation, and test results of the TMS reference system.
Related projects
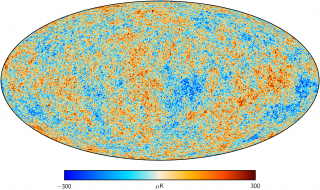
Anisotropy of the Cosmic Microwave Background
The general goal of this project is to determine and characterize the spatial and spectral variations in the temperature and polarisation of the Cosmic Microwave Background in angular scales from several arcminutes to several degrees. The primordial matter density fluctuations which originated the structure in the matter distribution of the present
Rafael
Rebolo López

QUIJOTE CMB Experiment (Q-U-I JOint TEnerife CMB Experiment)
QUIJOTE es un programa de dos telescopios y su batería de instrumentos, instalados en el Observatorio del Teide, dedicados fundamentalmente a la caracterización de la polarización del Fondo Cósmico de Microondas, en el rango de frecuencias de 10-42 GHz.
José Alberto
Rubiño Martín