Bibcode
Zacchei, A.; Zonca, A.; White, S. D. M.; Yvon, D.; Vittorio, N.; Wade, L. A.; Wandelt, B. D.; Welikala, N.; Van Tent, B.; Vielva, P.; Villa, F.; Tristram, M.; Tucci, M.; Valenziano, L.; Terenzi, L.; Toffolatti, L.; Tomasi, M.; Suur-Uski, A.-S.; Sygnet, J.-F.; Tauber, J. A.; Sudiwala, R.; Sunyaev, R.; Sutton, D.; Scott, D.; Smoot, G. F.; Starck, J.-L.; Sandri, M.; Savini, G.; Schaefer, B. M.; Rossetti, M.; Rubiño-Martín, J. A.; Rusholme, B.; Rocha, G.; Roman, M.; Rosset, C.; Ricciardi, S.; Riller, T.; Ristorcelli, I.; Reinecke, M.; Remazeilles, M.; Renault, C.; Rachen, J. P.; Rebolo, R.; Prunet, S.; Puget, J.-L.; Poutanen, T.; Pratt, G. W.; Ponthieu, N.; Popa, L.; Piffaretti, R.; Plaszczynski, S.; Pointecouteau, E.; Polenta, G.; Piacentini, F.; Piat, M.; Pierpaoli, E.; Perdereau, O.; Perotto, L.; Perrotta, F.; Paoletti, D.; Pasian, F.; Patanchon, G.; Novikov, D.; Novikov, I.; Osborne, S.; Pajot, F.; Nørgaard-Nielsen, H. U.; Noviello, F.; Nati, F.; Natoli, P.; Munshi, D.; Murphy, J. A.; Naselsky, P.; Montier, L.; Morgante, G.; Miville-Deschènes, M.-A.; Moneti, A.; Mennella, A.; Mitra, S.; Melin, J.-B.; Mendes, L.; Matthai, F.; Mazzotta, P.; Mei, S.; Melchiorri, A.; Massardi, M.; Matarrese, S.; Marshall, D. J.; Martínez-González, E.; Masi, S.; Maffei, B.; Maino, D.; Mandolesi, N.; Maris, M.; Marleau, F.; Lubin, P. M.; Luzzi, G.; Macías-Pérez, J. F.; Linden-Vørnle, M.; López-Caniego, M. et al.
Bibliographical reference
Astronomy and Astrophysics, Volume 550, id.A134, 16 pp.
Advertised on:
2
2013
Journal
Citations
104
Refereed citations
101
Description
Context. About half of the baryons of the Universe are expected to be in
the form of filaments of hot and low-density intergalactic medium. Most
of these baryons remain undetected even by the most advanced X-ray
observatories, which are limited in sensitivity to the diffuse
low-density medium. Aims: The Planck satellite has provided
hundreds of detections of the hot gas in clusters of galaxies via the
thermal Sunyaev-Zel'dovich (tSZ) effect and is an ideal instrument for
studying extended low-density media through the tSZ effect. In this
paper we use the Planck data to search for signatures of a fraction of
these missing baryons between pairs of galaxy clusters. Methods:
Cluster pairs are good candidates for searching for the hotter and
denser phase of the intergalactic medium (which is more easily observed
through the SZ effect). Using an X-ray catalogue of clusters and the
Planck data, we selected physical pairs of clusters as candidates. Using
the Planck data, we constructed a local map of the tSZ effect centred on
each pair of galaxy clusters. ROSAT data were used to construct X-ray
maps of these pairs. After modelling and subtracting the tSZ effect and
X-ray emission for each cluster in the pair, we studied the residuals on
both the SZ and X-ray maps. Results: For the merging cluster pair
A399-A401 we observe a significant tSZ effect signal in the intercluster
region beyond the virial radii of the clusters. A joint X-ray SZ
analysis allows us to constrain the temperature and density of this
intercluster medium. We obtain a temperature of kT = 7.1 ± 0.9
keV (consistent with previous estimates) and a baryon density of (3.7
± 0.2) × 10-4 cm-3.
Conclusions: The Planck satellite mission has provided the first SZ
detection of the hot and diffuse intercluster gas.
Related projects
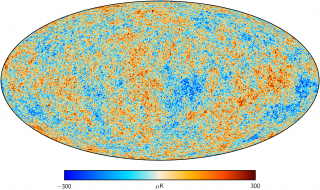
Anisotropy of the Cosmic Microwave Background
The general goal of this project is to determine and characterize the spatial and spectral variations in the temperature and polarisation of the Cosmic Microwave Background in angular scales from several arcminutes to several degrees. The primordial matter density fluctuations which originated the structure in the matter distribution of the present
Rafael
Rebolo López
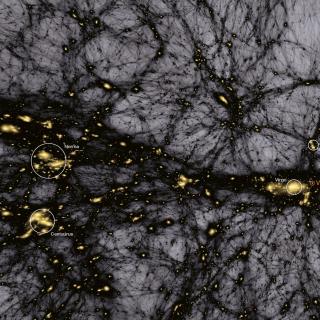
Cosmology with Large Scale Structure Probes
The Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) contains the statistical information about the early seeds of the structure formation in our Universe. Its natural counterpart in the local universe is the distribution of galaxies that arises as a result of gravitational growth of those primordial and small density fluctuations. The characterization of the
FRANCISCO SHU
KITAURA JOYANES