Bibcode
Lim, Chen-Fatt; Wang, Wei-Hao; Smail, Ian; Scott, Douglas; Chen, Chian-Chou; Chang, Yu-Yen; Simpson, James M.; Toba, Yoshiki; Shu, Xinwen; Clements, Dave; Greenslade, Josh; Ao, YiPing; Babul, Arif; Birkin, Jack; Chapman, Scott C.; Cheng, Tai-An; Cho, Brian S.; Dannerbauer, Helmut; Dudzevičiūtė, Ugnė; Dunlop, James; Gao, Yu; Goto, Tomotsugu; Ho, Luis C.; Hsu, Li-Ting; Hwang, Ho Seong; Jeong, Woong-Seob; Koprowski, Maciej; Lee, Chien-Hsiu; Lin, Ming-Yi; Lin, Wei-Ching; Michałowski, Michał J.; Parsons, Harriet; Sawicki, Marcin; Shirley, Raphael; Shim, Hyunjin; Urquhart, Sheona; Wang, Jianfa; Wang, Tao
Bibliographical reference
The Astrophysical Journal
Advertised on:
2
2020
Journal
Citations
34
Refereed citations
31
Description
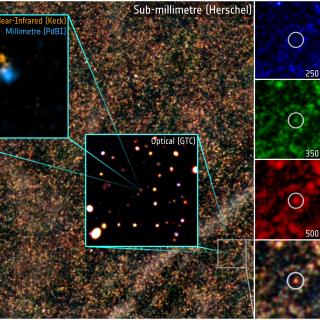
We construct a SCUBA-2 450 μm map in the COSMOS field that covers an area of 300 arcmin2 and reaches a 1σ noise level of 0.65 mJy in the deepest region. We extract 256 sources detected at 450 μm with signal-to-noise ratios >4.0 and analyze the physical properties of their multiwavelength counterparts. We find that most of the sources are at z ≲ 3, with a median of $z={1.79}_{-0.15}^{+0.03} \% $ . About ${35}_{-25}^{+32} \% $ of our sources are classified as starburst galaxies based on their total star formation rates (SFRs) and stellar masses (M*). By fitting the far-infrared spectral energy distributions, we find that our 450 μm selected sample has a wide range of dust temperatures (20 K ≲ Td ≲ 60 K), with a median of ${T}_{{\rm{d}}}={38.3}_{-0.9}^{+0.4}$ K. We do not find a redshift evolution in dust temperature for sources with ${L}_{\mathrm{IR}}\gt {10}^{12}\,{L}_{\odot }$ at z < 3. However, we find a moderate correlation where the dust temperature increases with the deviation from the SFR─M* relation. The increase in dust temperature also correlates with optical morphology, which is consistent with merger-triggered starbursts in submillimeter galaxies. Our galaxies do not show the tight IRX─βUV correlation that has been observed in the local universe. We construct the infrared luminosity functions of our 450 μm sources and measure their comoving SFR densities (SFRDs). The contribution of the ${L}_{\mathrm{IR}}\gt {10}^{12}\,{L}_{\odot }$ population to the SFRD rises dramatically from z = 0 to 2 (∝(1 + z)3.9±1.1) and dominates the total SFRD at z ≳ 2.
Related projects
Formation and Evolution of Galaxies: Observations in Infrared and other Wavelengths
This IAC research group carries out several extragalactic projects in different spectral ranges, using space as well as ground-based telescopes, to study the cosmological evolution of galaxies and the origin of nuclear activity in active galaxies. The group is a member of the international consortium which built the SPIRE instrument for the
Ismael
Pérez Fournon

Molecular Gas and Dust in Galaxies Across Cosmic Time
Two of the most fundamental questions in astrophysics are the conversion of molecular gas into stars and how this physical process is a function of environments on all scales, ranging from planetary systems, stellar clusters, galaxies to galaxy clusters. The main goal of this internal project is to get insight into the formation and evolution of
Helmut
Dannerbauer