Bibcode
Ma, J.; Brown, Arianna; Cooray, Asantha; Nayyeri, Hooshang; Messias, Hugo; Timmons, Nicholas; Staguhn, Johannes; Temi, Pasquale; Dowell, C. Darren; Wardlow, Julie; Fadda, Dario; Kovacs, Attila; Riechers, Dominik; Oteo, Ivan; Wilson, Derek; Perez-Fournon, I.
Bibliographical reference
The Astrophysical Journal, Volume 864, Issue 1, article id. 60, 8 pp. (2018).
Advertised on:
9
2018
Journal
Citations
3
Refereed citations
2
Description
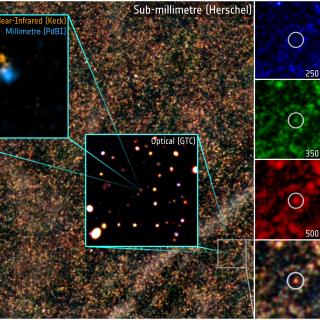
We present the detection at 89 μm (observed frame) of the
Herschel-selected gravitationally lensed starburst galaxy HATLAS
J1429-0028 (also known as G15v2.19) in 15 minutes with the
High-resolution Airborne Wideband Camera-plus (HAWC+) onboard the
Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA). The
spectacular lensing system consists of an edge-on foreground disk galaxy
at z = 0.22 and a nearly complete Einstein ring of an intrinsic
ultra-luminous infrared (IR) galaxy at z = 1.03. Is this high IR
luminosity powered by pure star formation (SF) or also an active
galactic nucleus (AGN)? Previous nebular line diagnostics indicate that
it is star formation dominated. We perform a 27-band multiwavelength
spectral energy distribution (SED) modeling including the new
SOFIA/HAWC+ data to constrain the fractional AGN contribution to the
total IR luminosity. The AGN fraction in the IR turns out to be
negligible. In addition, J1429-0028 serves as a testbed for comparing
SED results from different models/templates and SED codes (MAGPHYS,
SED3FIT, and CIGALE). We stress that star formation history is the
dominant source of uncertainty in the derived stellar mass (as high as a
factor of ∼10) even in the case of extensive photometric coverage.
Furthermore, the detection of a source at z ∼ 1 with SOFIA/HAWC+
demonstrates the potential of utilizing this facility for distant galaxy
studies including the decomposition of SF/AGN components, which cannot
be accomplished with other current facilities.
Related projects
Formation and Evolution of Galaxies: Observations in Infrared and other Wavelengths
This IAC research group carries out several extragalactic projects in different spectral ranges, using space as well as ground-based telescopes, to study the cosmological evolution of galaxies and the origin of nuclear activity in active galaxies. The group is a member of the international consortium which built the SPIRE instrument for the
Ismael
Pérez Fournon