Bibcode
Dhawan, S.; Pierel, J. D. R.; Gu, M.; Newman, A. B.; Larison, C.; Siebert, M.; Petrushevska, T.; Poidevin, F.; Jha, S. W.; Chen, W.; Ellis, Richard S.; Frye, B.; Hjorth, J.; Koekemoer, Anton M.; Pérez-Fournon, I.; Rest, A.; Treu, T.; Windhorst, R. A.; Zenati, Y.
Bibliographical reference
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
Advertised on:
12
2024
Citations
6
Refereed citations
1
Description
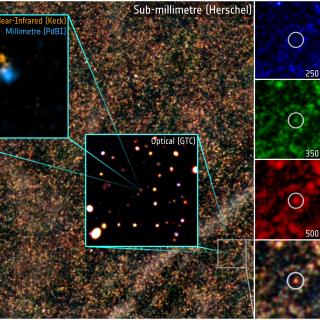
Strong gravitational lensing magnifies the light from a background source, allowing us to study these sources in detail. Here, we study the spectra of a $z = 1.95$ lensed Type Ia supernova (SN Ia) SN Encore for its brightest image A, taken 39 d apart. We infer the spectral age with template matching using the supernova identification (SNID ) software and find the spectra to be at $29.0 \pm 5.0$ and $37.4 \pm 2.8$ rest-frame days post-maximum, respectively, consistent with separation in the observer frame after accounting for time dilation. Since SNe Ia measure dark energy properties by providing relative distances between low- and high-z SNe, it is important to test for the evolution of spectroscopic properties. Comparing the spectra to composite low-z SN Ia spectra, we find strong evidence of the similarity between the local sample and SN Encore. The line velocities of common SN Ia spectral lines, Si II 6355 $\mathring{\rm A}$ and Ca II near-infrared triplet, are consistent with the distribution for the low-z sample as well as other lensed SNe Ia, e.g. iPTF16geu ($z = 0.409$) and SN H0pe ($z = 1.78$). The consistency between the low-z sample and lensed SNe at high-z suggests no obvious cosmic evolution demonstrating their use as high-z distance indicators, though this needs to be confirmed/refuted via a larger sample. We also find that the spectra of SN Encore match the predictions for explosion models very well. With future large samples of lensed SNe Ia, e.g. with the Vera C. Rubin Observatory, spectra at such late phases will be important to distinguish between different explosion scenarios.
Related projects

Molecular Gas and Dust in Galaxies Across Cosmic Time
Two of the most fundamental questions in astrophysics are the conversion of molecular gas into stars and how this physical process is a function of environments on all scales, ranging from planetary systems, stellar clusters, galaxies to galaxy clusters. The main goal of this internal project is to get insight into the formation and evolution of
Helmut
Dannerbauer
Formation and Evolution of Galaxies: Observations in Infrared and other Wavelengths
This IAC research group carries out several extragalactic projects in different spectral ranges, using space as well as ground-based telescopes, to study the cosmological evolution of galaxies and the origin of nuclear activity in active galaxies. The group is a member of the international consortium which built the SPIRE instrument for the
Ismael
Pérez Fournon