Bibcode
Nashimoto, Masashi; Hattori, Makoto; Génova-Santos, Ricardo; Poidevin, Frédérick
Bibliographical reference
Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan
Advertised on:
2
2020
Citations
6
Refereed citations
6
Description
Complete studies of the radiative processes of thermal emission from the amorphous dust from microwave through far-infrared wavebands are presented by taking into account, self-consistently for the first time, the standard two-level systems (TLS) model of amorphous materials. The observed spectral energy distributions (SEDs) for the Perseus molecular cloud (MC) and W 43 from microwave through far-infrared are fitted with the SEDs calculated with the TLS model of amorphous silicate. We have found that the model SEDs reproduce the observed properties of the anomalous microwave emission (AME) well. The present result suggests an alternative interpretation for the AME being carried by the resonance emission of the TLS of amorphous materials without introducing new species. Simultaneous fitting of the intensity and polarization SEDs for the Perseus MC and W 43 are also performed. The amorphous model reproduces the overall observed feature of the intensity and polarization SEDs of the Perseus MC and W 43. However, the model's predicted polarization fraction of the AME is slightly higher than the QUIJOTE upper limits in several frequency bands. A possible improvement of our model to resolve this problem is proposed. Our model predicts that interstellar dust is amorphous materials with very different physical characteristics compared with terrestrial amorphous materials.
Related projects
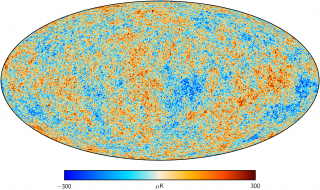
Anisotropy of the Cosmic Microwave Background
The general goal of this project is to determine and characterize the spatial and spectral variations in the temperature and polarisation of the Cosmic Microwave Background in angular scales from several arcminutes to several degrees. The primordial matter density fluctuations which originated the structure in the matter distribution of the present
Rafael
Rebolo López
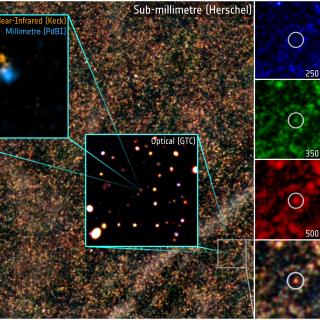
Formation and Evolution of Galaxies: Observations in Infrared and other Wavelengths
This IAC research group carries out several extragalactic projects in different spectral ranges, using space as well as ground-based telescopes, to study the cosmological evolution of galaxies and the origin of nuclear activity in active galaxies. The group is a member of the international consortium which built the SPIRE instrument for the
Ismael
Pérez Fournon