Bibcode
DOI
Rodríguez-González, A.; Esquivel, A.; Velázquez, P. F.; Raga, A. C.; Melo, V.
Referencia bibliográfica
The Astrophysical Journal, Volume 689, Issue 1, pp. 153-159.
Fecha de publicación:
12
2008
Revista
Número de citas
9
Número de citas referidas
8
Descripción
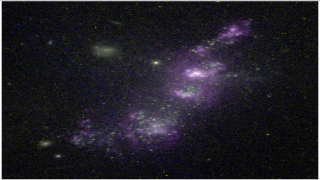
The starburst galaxy M82 shows a system of Hα-emitting filaments
that extend to each side of the galactic disk. We model these filaments
as the result of the interaction between the winds from a distribution
of super stellar clusters (SSCs). We first derive the condition
necessary for producing a radiative interaction between the cluster
winds (a condition that is met by the SSC distribution of M82). We then
compute three-dimensional (3D) simulations for SSC wind distributions
that satisfy the condition for a radiative interaction, as well as for
distributions that do not satisfy this condition. We find that the
highly radiative models, which result from the interaction of
high-metallicity cluster winds, produce a structure of Hα-emitting
filaments that qualitatively agrees with the observations of M82, while
the nonradiative SSC wind interaction models do not produce filamentary
structures. Therefore, our criterion for radiative interactions (which
depends on the mass-loss rate, the terminal velocity of the SSC winds,
and the mean separation between the SSCs) can be used to predict whether
or not an observed galaxy should have associated Hα-emitting
filaments.
Proyectos relacionados
Grupo de Estudios de Formación Estelar GEFE
El proyecto interno GEFE está enmarcado en el proyecto coordinado, ESTALLIDOS, financiado por el plan nacional desde el año 2001. El ultimo proyecto aprobado es ESTALLIDOS 6.0 (AYA2016- 79724-C4-2-P). En el proyecto GEFE trabajamos en base al caso científico del proyecto ESTALLIDOS 6.0. Los estallidos de formación estelar (Starbursts o SB) son
Casiana
Muñoz Tuñón