Bibcode
Queiroz, Carolina; Abramo, L. Raul; Rodrigues, Natália V. N.; Pérez-Ràfols, Ignasi; Martínez-Solaeche, Ginés; Hernán-Caballero, Antonio; Hernández-Monteagudo, Carlos; Lumbreras-Calle, Alejandro; Pieri, Matthew M.; Morrison, Sean S.; Bonoli, Silvia; Chaves-Montero, Jonás; Chies-Santos, Ana L.; Díaz-García, L. A.; Fernandez-Soto, Alberto; González Delgado, Rosa M.; Alcaniz, Jailson; Benítez, Narciso; Javier Cenarro, A.; Civera, Tamara; Dupke, Renato A.; Ederoclite, Alessandro; López-Sanjuan, Carlos; Marín-Franch, Antonio; Mendes de Oliveira, Claudia; Moles, Mariano; Muniesa, David; Sodré, Laerte; Taylor, Keith; Varela, Jesús; Vázquez Ramió, Héctor
Referencia bibliográfica
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
Fecha de publicación:
4
2023
Número de citas
14
Número de citas referidas
14
Descripción
In this series of papers, we employ several machine learning (ML) methods to classify the point-like sources from the miniJPAS catalogue, and identify quasar candidates. Since no representative sample of spectroscopically confirmed sources exists at present to train these ML algorithms, we rely on mock catalogues. In this first paper, we develop a pipeline to compute synthetic photometry of quasars, galaxies, and stars using spectra of objects targeted as quasars in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. To match the same depths and signal-to-noise ratio distributions in all bands expected for miniJPAS point sources in the range 17.5 ≤ r < 24, we augment our sample of available spectra by shifting the original r-band magnitude distributions towards the faint end, ensure that the relative incidence rates of the different objects are distributed according to their respective luminosity functions, and perform a thorough modelling of the noise distribution in each filter, by sampling the flux variance either from Gaussian realizations with given widths, or from combinations of Gaussian functions. Finally, we also add in the mocks the patterns of non-detections which are present in all real observations. Although the mock catalogues presented in this work are a first step towards simulated data sets that match the properties of the miniJPAS observations, these mocks can be adapted to serve the purposes of other photometric surveys.
Proyectos relacionados
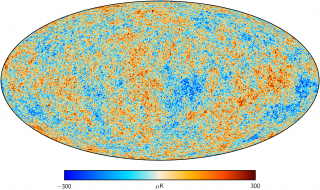
Anisotropía del Fondo Cósmico de Microondas
El objetivo general de este proyecto es determinar y estudiar las variaciones espaciales y espectrales en la temperatura del Fondo Cósmico de Microondas y en su Polarización en un amplio rango de escalas angulares que van desde pocos minutos de arco hasta varios grados. Las fluctuaciones primordiales en la densidad de materia, que dieron origen a
Rafael
Rebolo López
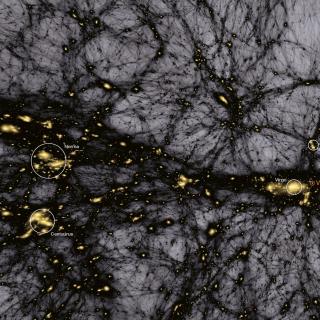
Cosmología con Trazadores de la Estructura a Gran Escala del Universo
El Fondo Cósmico de Microondas (FCM) contiene la información estadística de las semillas primigenias que han dado lugar a la formación de todas las estructuras en el Universo. Su contrapartida natural en el Universo local es la distribución de las galaxias que surgen como resultado del crecimiento gravitatorio de aquellas fluctuaciones de densidad
FRANCISCO SHU
KITAURA JOYANES