Subvenciones relacionadas:
General
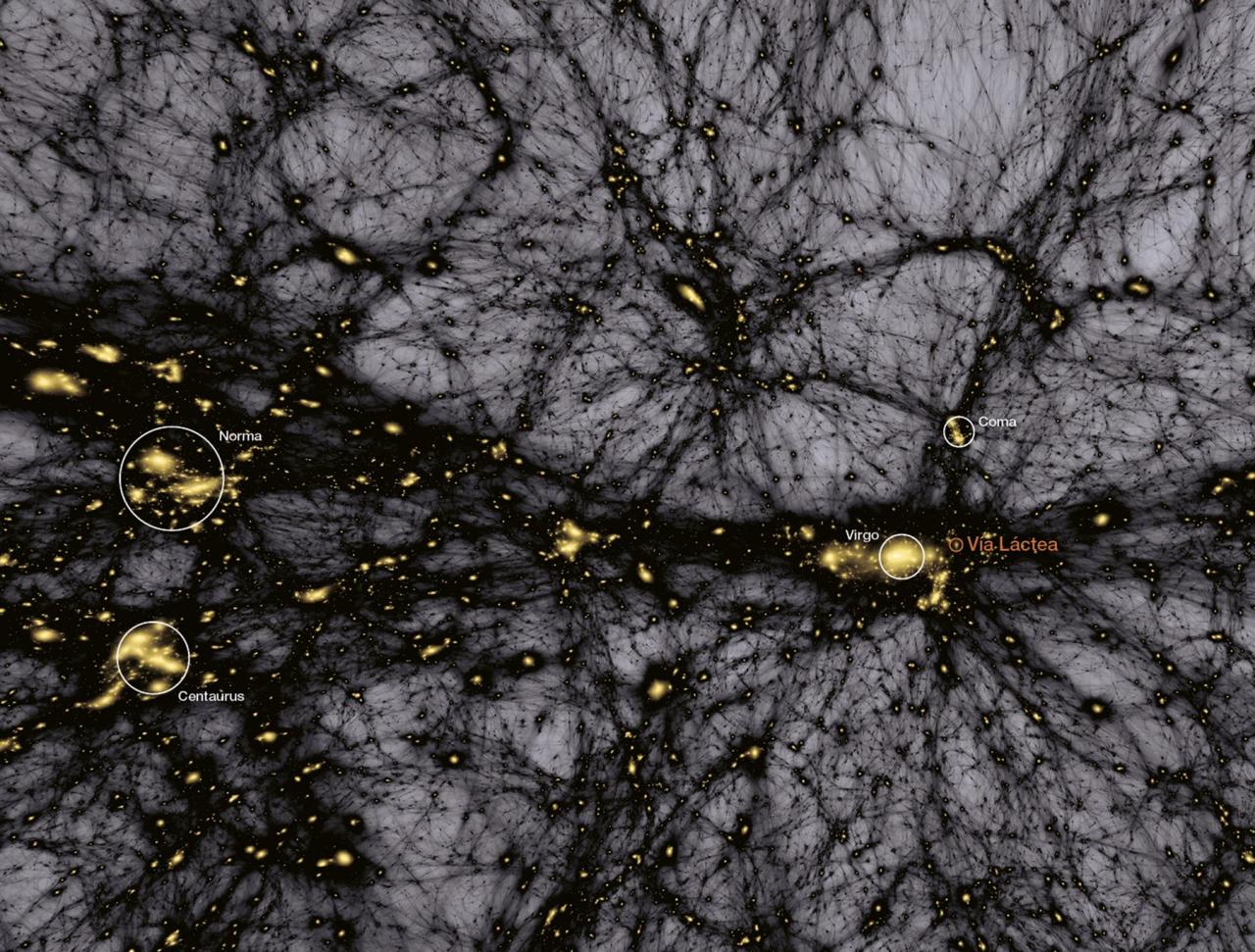
El Fondo Cósmico de Microondas (FCM) contiene la información estadística de las semillas primigenias que han dado lugar a la formación de todas las estructuras en el Universo. Su contrapartida natural en el Universo local es la distribución de las galaxias que surgen como resultado del crecimiento gravitatorio de aquellas fluctuaciones de densidad primigenias. La caracterización de la distribución de inhomogeneidades a gran escala en el Universo local proporciona una herramienta muy poderosa, y complementaria al FCM, para determinar el origen y el contenido energético del Universo, el ritmo de expansión del mismo durante la evolución cósmica, los detalles del proceso de formación de todas las estructuras a gran escala que observamos en el Universo hoy día. Esta es la página web del grupo de Cosmología con trazadores de la Estructura a Gran Escala (LSS de sus siglas en inglés), en el IAC.
Miembros
Resultados
- eBOSS: análisis cosmológico de los datos de cuásares. Marcos Pellejero Ibañez and F. S. Kitaura participaron en la construcción de la likelihood y en el análisis de los parámetros cosmológicos (including as coauthors Kitaura & Pellejero Ibañez: 2018MNRAS.473.4773A).
- EUCLID: proyecto comparativo de códigos para generar catálogos de galaxias sintéticos, donde se demostró la precisión y eficiencia de PATCHY (including as coauthors Balaguera-Antolínez, Kitaura & Pellejero Ibañez: https://arxiv.org/abs/1806.09497, https://arxiv.org/abs/1806.09477, https://arxiv.org/abs/1806.09499)
- Desarrollo de un método para asignar el bias para estudios de estructura a gran escala (Balaguera-Antolínez, Kitaura, Pellejero Ibañez et al 2018: https://arxiv.org/abs/1806.05870)
- Presentación del proyecto UNITSIM para proporcionar modelos teóricos para comparar con observaciones DESI y EUCLID (including as coauthors Kitaura & Pellejero Ibañez:http://www.unitsims.org/ https://arxiv.org/abs/1811.02111)
- Presentación del código BARCODE (Bos, Kitaura & Weygaert 2018: https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.05189, http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2018ascl.soft10002B)
Actividad científica
Publicaciones relacionadas
No se han encontrado publicaciones relacionadas.Charlas relacionadas
No se han encontrado charlas relacionadas.Congresos relacionados
-
 XXXIII Escuela de Invierno de Canarias sobre Astrofísica: Física de Astropartículas y CosmologíaLa XXXIII Canary Islands Winter School of Astrophysics, organizada por el Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC), se centra en la Física de Partículas y la Cosmología. La escuela, que se celebrará"Salón de actos" del Museo de la Ciencia y el Cosmos (MCC) Avda. Los Menceyes 70 38205 San Cristóbal de La LagunaEspañaFecha-Anteriores
XXXIII Escuela de Invierno de Canarias sobre Astrofísica: Física de Astropartículas y CosmologíaLa XXXIII Canary Islands Winter School of Astrophysics, organizada por el Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC), se centra en la Física de Partículas y la Cosmología. La escuela, que se celebrará"Salón de actos" del Museo de la Ciencia y el Cosmos (MCC) Avda. Los Menceyes 70 38205 San Cristóbal de La LagunaEspañaFecha-Anteriores