Subvenciones relacionadas:
General
Este grupo desarrolla varios proyectos extragalácticos en diferentes rangos del espectro electromagnético utilizando satélites y telescopios en tierra para estudiar la evolución cosmológica de las galaxias y el origen de la actividad nuclear en galaxias activas. En el aspecto instrumental, el grupo forma parte del consorcio internacional que ha construido el instrumento SPIRE del Observatorio Espacial Herschel y del consorcio europeo que desarrolla el instrumento SAFARI para el telescopio espacial infrarrojo SPICA de las agencias espaciales ESA y JAXA.
Los proyectos principales en 2018 han sido:
a) Galaxias y cuásares distantes con emisión en el infrarrojo lejano descubiertas con el Observatorio Espacial Herschel en los "Key Projects" HerMES y Herschel-ATLAS.
b) Sloan Digital Sky Survey IV: galaxias del proyecto BELLS GALLERY y galaxias Lyman alpha muy luminosas
c) Participación en el desarrollo del instrumento SAFARI, una de las contribuciones europeas al telescopio espacial infrarrojo SPICA.
d) Descubrimiento de la estrella individual más distante conocida, en uno de los campos del proyecto "HST Frontier Fields"
e) Búsqueda de supernovas en galaxias distantes amplificadas por lentes gravitacionales.
f) Varios estudios con GTC de sistemas de absorción en la línea de visión a cuásares rojos.
Miembros
Resultados
- Marques-Chaves et al. (2018) presentan un estudio detallado de la galaxia submm HLock01 a z = 2.9574, una de las fuentes más brillantes magnificadas por una lente gravitacional descubiertas en el "Herschel Multi-tiered Extragalactic Survey".
- Rigopoulou et al. (2018) derivan la metalicidad de la fase gaseosa de la galaxia submm HLSW-01 utilizando observaciones espectroscópicas de líneas de estructura fina con Herschel. Encuentran que la metalicidad de galaxias submm luminosas es de tipo solar y que siguen la relación masa-metalicidad esperada para galaxias a z ∼ 3.
- Cornachione et al. (2018) presentan un estudio morfológico de 17 galaxias emisoras Lyman alpha magnificadas por lentes gravitacionales de la muestra BELLS GALLERY. El análisis combina el efecto de magnificación de las lentes fuertes galaxia-galaxia con la alta resolución angular del telescopio espacial Hubble para conseguir una resolución espacial de ~80 pc.
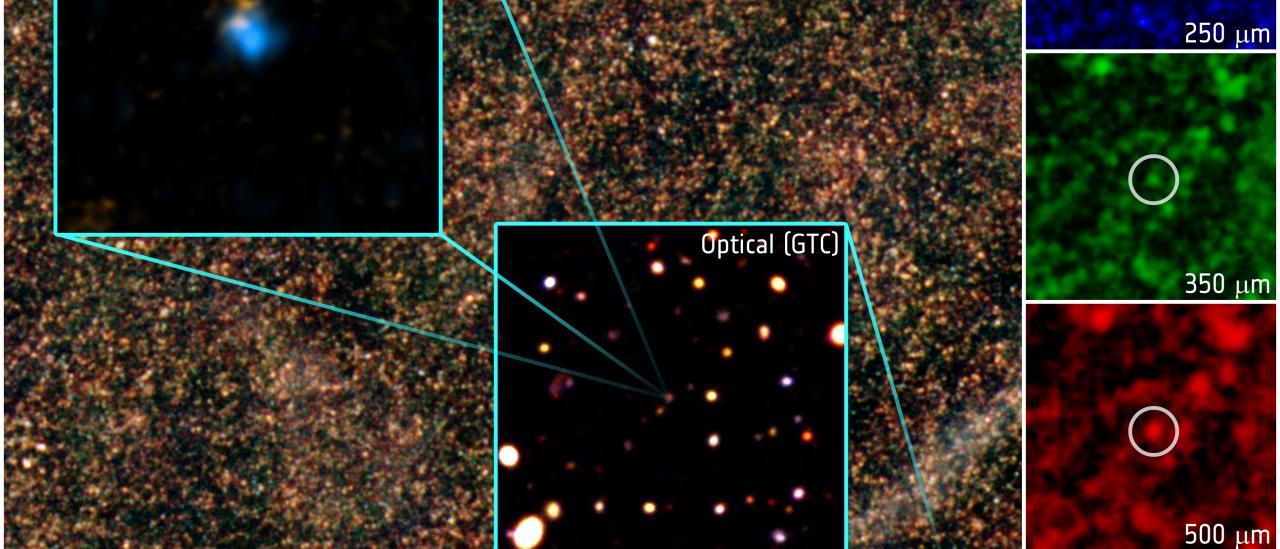
- Oteo et al. (2018) reportan la identificación de un protocúmulo de galaxias extremo en el universo temprano cuyo núcleo (denominado Núcleo Rojo Distante por su color muy rojo en las bandas de Herschel SPIRE) está formado por al menos 10 galaxias polvorientas con formación estelar, confirmadas espectroscópicamente a z = 4.002 con ALMA y ATCA.
- Kelly et al. (2018) reportan el descubrimiento de una estrella individual, Icarus, a un desplazamiento al rojo de 1.49, magnificada más de 2000 veces por el efecto de lente gravitacional del cúmulo de galaxias MACS J1149+222. Icarus está localizada en una galaxia espiral muy alejada de la tierra, su luz ha tardado 9000 millones de años en llegar a la tierra.