Bibcode
Page, M. J.; Symeonidis, M.; Vieira, J. D.; Altieri, B.; Amblard, A.; Arumugam, V.; Aussel, H.; Babbedge, T.; Blain, A.; Bock, J.; Boselli, A.; Buat, V.; Castro-Rodríguez, N.; Cava, A.; Chanial, P.; Clements, D. L.; Conley, A.; Conversi, L.; Cooray, A.; Dowell, C. D.; Dubois, E. N.; Dunlop, J. S.; Dwek, E.; Dye, S.; Eales, S.; Elbaz, D.; Farrah, D.; Fox, M.; Franceschini, A.; Gear, W.; Glenn, J.; Griffin, M.; Halpern, M.; Hatziminaoglou, E.; Ibar, E.; Isaak, K.; Ivison, R. J.; Lagache, G.; Levenson, L.; Lu, N.; Madden, S.; Maffei, B.; Mainetti, G.; Marchetti, L.; Nguyen, H. T.; O'Halloran, B.; Oliver, S. J.; Omont, A.; Panuzzo, P.; Papageorgiou, A.; Pearson, C. P.; Pérez-Fournon, I.; Pohlen, M.; Rawlings, J. I.; Rigopoulou, D.; Riguccini, L.; Rizzo, D.; Rodighiero, G.; Roseboom, I. G.; Rowan-Robinson, M.; Portal, M. Sánchez; Schulz, B.; Scott, D.; Seymour, N.; Shupe, D. L.; Smith, A. J.; Stevens, J. A.; Trichas, M.; Tugwell, K. E.; Vaccari, M.; Valtchanov, I.; Viero, M.; Vigroux, L.; Wang, L.; Ward, R.; Wright, G.; Xu, C. K.; Zemcov, M.
Referencia bibliográfica
Nature, Volume 485, Issue 7397, pp. 213-216 (2012).
Fecha de publicación:
5
2012
Revista
Número de citas
186
Número de citas referidas
177
Descripción
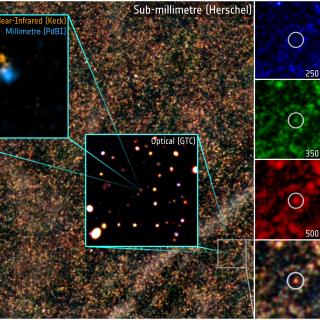
The old, red stars that constitute the bulges of galaxies, and the
massive black holes at their centres, are the relics of a period in
cosmic history when galaxies formed stars at remarkable rates and active
galactic nuclei (AGN) shone brightly as a result of accretion onto black
holes. It is widely suspected, but unproved, that the tight correlation
between the mass of the black hole and the mass of the stellar bulge
results from the AGN quenching the surrounding star formation as it
approaches its peak luminosity. X-rays trace emission from AGN
unambiguously, whereas powerful star-forming galaxies are usually
dust-obscured and are brightest at infrared and submillimetre
wavelengths. Here we report submillimetre and X-ray observations that
show that rapid star formation was common in the host galaxies of AGN
when the Universe was 2-6 billion years old, but that the most vigorous
star formation is not observed around black holes above an X-ray
luminosity of 1044 ergs per second. This suppression of star
formation in the host galaxy of a powerful AGN is a key prediction of
models in which the AGN drives an outflow, expelling the interstellar
medium of its host and transforming the galaxy's properties in a brief
period of cosmic time.
Proyectos relacionados
Formación y Evolución de Galaxias: Observaciones Infrarrojas y en otras Longitudes de Onda
Este grupo desarrolla varios proyectos extragalácticos en diferentes rangos del espectro electromagnético utilizando satélites y telescopios en tierra para estudiar la evolución cosmológica de las galaxias y el origen de la actividad nuclear en galaxias activas. En el aspecto instrumental, el grupo forma parte del consorcio internacional que ha
Ismael
Pérez Fournon