Subvenciones relacionadas:
General
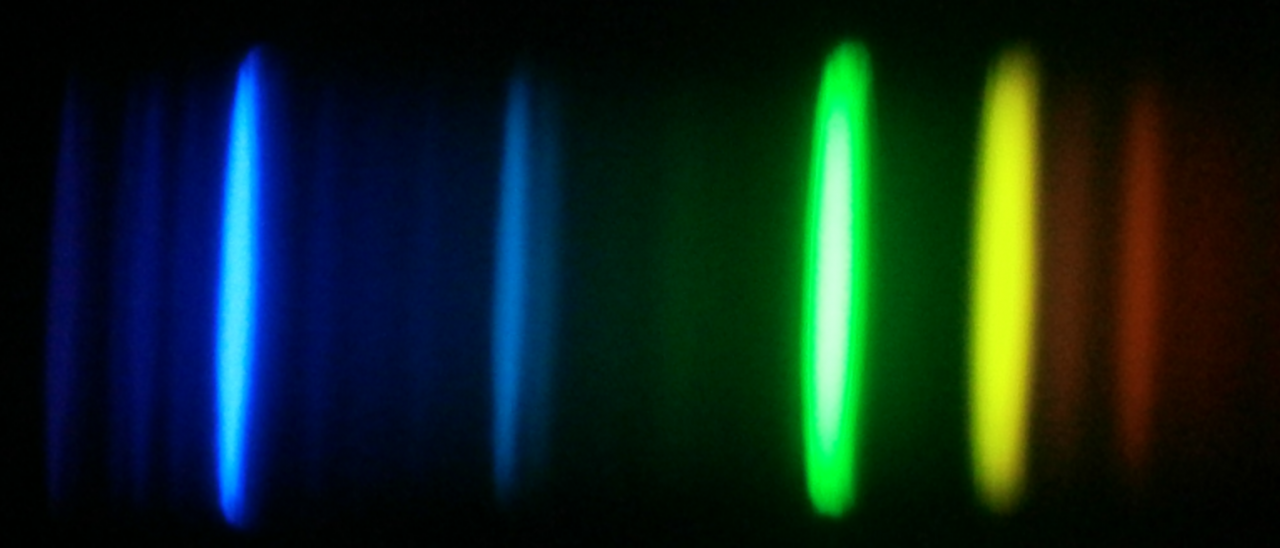
La espectroscopía de estrellas nos permite determinar las propiedades y composiciones químicas de las mismas. A partir de esta información para estrellas de diferente edad en la Vía Láctea es posible reconstruir la evolución química de la Galaxia, así como el origen de los elementos más pesados que el boro, forjados principalmente en los interiores estelares. También es posible estudiar la formación estelar, y la de la propia Galaxia, a través de la huella que deja el potencial Galáctico en las órbitas de las estrellas, y de las distribuciones de masa, edad y la abundancia de elementos pesados.
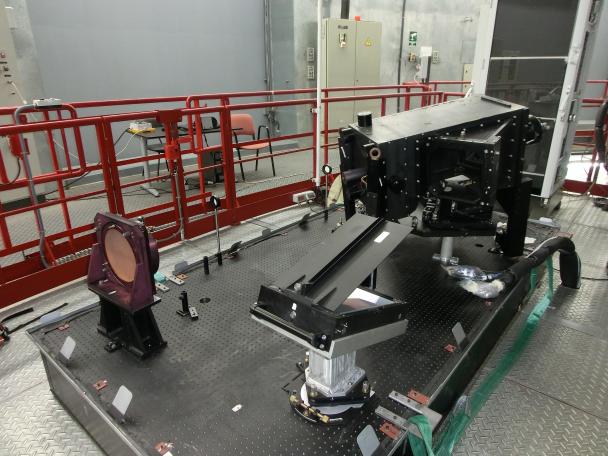
La obtención de espectros con alta resolución espectral, apropiados para estudios de la composición química, requiere instrumentación sofisticada y eficiente. Esto es especialmente cierto en investigaciones en las que se necesitan extensas muestras de estrellas, que exigen observar cientos, o incluso miles de fuentes de forma simultánea. El procesado y análisis de los datos debe ser automatizado para ser igualmente eficiente.
La interpretación de los espectros se basa en modelos físicos de las atmósferas de las estrellas, de donde se escapa la luz que observamos. Los ingredientes fundamentales para la construcción de estos modelos son la dinámica de fluidos, y las propiedades de los átomos, iones y moléculas, especialmente en lo que se refiere a sus interacciones con la radiación que proviene del interior estelar. Una vez que se tiene un modelo plausible, es posible calcular de forma detallada cómo se propaga la radiación a través de la atmósfera estelar, y el espectro emergente, para, de forma iterativa, compararlo con las observaciones y refinar el modelo.
Este Proyecto incluye tres diferentes frentes de investigación:
- La mejora de los modelos de atmósfera y las simulaciones de espectros estelares.
- El desarrollo de herramientas para la obtención, reducción y el análisis de observaciones espectroscópicas, y en particular para la determinación de abundancias químicas en estrellas.
- El diseño, preparación, y ejecución de estudios espectroscópicos de estrellas con el fin de entender a) los aspectos más relevantes de la física de las atmósferas estelares, b) la formación y evolución de las estrellas, c) el origen de los elementos químicos y d) la formación, estructura y evolución química de la Vía Láctea.
Miembros
Resultados
- Completar la instalación y pruebas de HORuS en GTC
- Descubrir dos nuevas estrellas con abundancias de hierro inferiores a 100.000 veces el valor solar
- Completar la clasificación de los espectros de APOGEE con K-means
- Publicar una colección completa de espectros modelo para estrellas O a M
- Identificar la huella de la difusión química en las atmósferas de estrellas del cúmulo M67
Actividad científica
Publicaciones relacionadas
Charlas relacionadas
No se han encontrado charlas relacionadas.Congresos relacionados
No se han encontrado congresos relacionados.