Tabernero, H. M.; Marfil, E.; Montes, D.; González Hernández, J. I.
Referencia bibliográfica
Astronomy and Astrophysics, Volume 628, id.A131, 12 pp.
Fecha de publicación:
8
2019
Revista
Número de citas
35
Número de citas referidas
31
Descripción
Context. STEPAR is an automatic code written in Python 3.X designed to
compute the stellar atmospheric parameters Teff, log g,
[Fe/H], and ξ of FGK-type stars by means of the equivalent width (EW)
method. This code has already been extensively tested in different
spectroscopic studies of FGK-type stars with several spectrographs and
against thousands of Gaia-ESO Survey UVES U580 spectra of late-type,
low-mass stars as one of its 13 pipelines. Aims: We describe the
code that we tested against a library of well characterised Gaia
benchmark stars. We also release the code to the community and provide
the link for download. Methods: We carried out the required EW
determination of Fe I and Fe II spectral lines using the automatic tool
TAME. STEPAR implements a grid of MARCS model atmospheres and the MOOG
radiative transfer code to compute stellar atmospheric parameters by
means of a Downhill Simplex minimisation algorithm. Results: We
show the results of the benchmark star test and also discuss the
limitations of the EW method, and hence the code. In addition, we find a
small internal scatter for the benchmark stars of 9 ± 32 K in
Teff, 0.00 ± 0.07 dex in log g, and 0.00 ± 0.03
dex in [Fe/H]. Finally, we advise against using STEPAR on double-lined
spectroscopic binaries or spectra with R < 30 000, S/N < 20, or v
sin i > 15 km s-1, and on stars later than K4 or earlier
than F6.
Proyectos relacionados

Pruebas Observacionales de los Procesos de Nucleosíntesis en el Universo
Recientemente se han llevado a cabo varios análisis espectroscópicos de estrellas con planetas. Uno de los resultados más relevantes ha sido descubrir que las estrellas con planetas son en promedio más metálicas que las estrellas del mismo tipo espectral sin planetas conocidos (Santos, Israelian & Mayor 2001, A&A, 373, 1019; 2004, A&A, 415, 1153)
Garik
Israelian
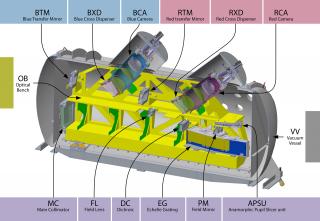
ARES: Alta Resolución ESpectral
ARES (Alta Resolución ESpectral) es un proyecto coordinado que pretende unificar y consolidar el esfuerzo del IAC en la investigación de alta resolución espectral, impulsando programas científicos frontera que el IAC desarrolla en el ámbito de exoplanetas, poblaciones estelares y cosmología, usando espectroscopía ultraestable de alta resolución.
Jonay Isai
González Hernández