Subvenciones relacionadas:
General
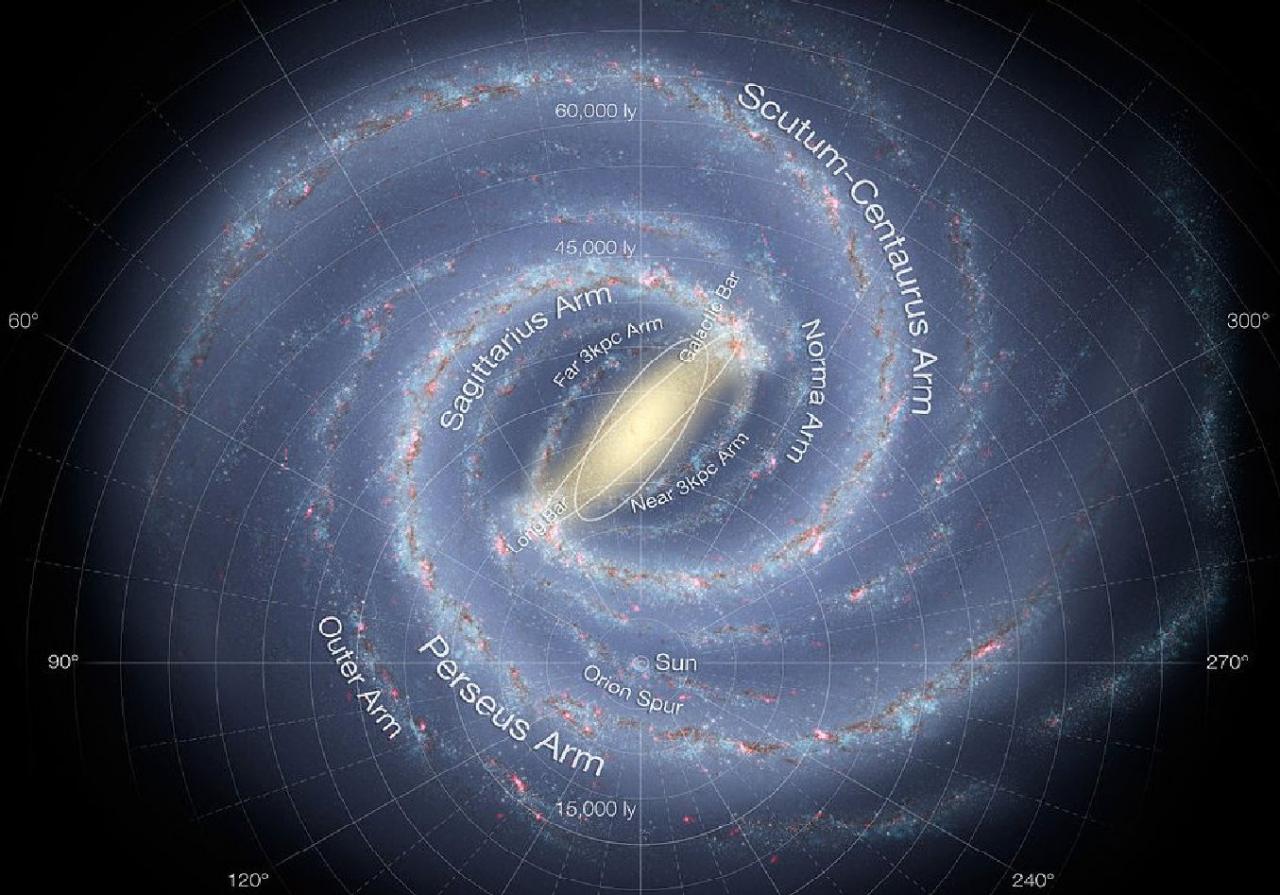
El Proyecto se estructura en dos partes, diferenciadas pero complementarias: morfología y dinámica. El estudio detallado de la morfología de la Vía Láctea pretende proveer una base de datos de distribución estelar en las regiones más alejadas y extintas de nuestra Galaxia, mediante el desarrollo de modelos semiempíricos a partir de la información contenida en dichos catálogos. Por otra parte, los análisis cinemáticos y dinámicos pretenden hacernos entender el origen de esos rasgos que observamos.
Nuestro grupo ha utilizado la combinación de datos propios (que incluirán en el futuro observaciones espectroscópicas con GRANTECAN/EMIR) con los catálogos públicos fotométricos (DENIS, 2MASS, UKIDSS, VISTA en infrarrojo cercano o SDSS) o espectroscópicos (SDSS-APOGEE en infrarrojo cercano, LAMOST). Se cuenta con información detallada de la distribución estelar de las poblaciones dominantes en una amplia zona de cielo, abarcando diferentes componentes estructurales: bulbo triaxial, barra larga, disco, brazos espirales, etc. Las componentes de gas y polvo son también objeto de estudio en infrarrojo, o en microondas (estudios de contaminación Galáctica al fondo cósmico de microondas, por ejemplo con WMAP o PLANCK). El grupo de investigación se ha integrado también en el nodo español de Gaia con la idea de orientar parte de nuestro trabajo en el aprovechamiento científico de la misión y, en concreto, en la identificación y estudio de poblaciones estelares a gran escala en la Galaxia.
Miembros
Resultados
- Disco de la Vía Láctea mucho mayor de lo que se pensaba. Ver nota de prensa del IAC: http://www.iac.es/divulgacion.php?op1=16&id=1385
Actividad científica
Publicaciones relacionadas
-
Transformations between the 2MASS, SDSS, and BV I photometric systems for late-type giantsWe present colour transformations from Two Micron All Sky Survey (2MASS) photometric system to Johnson-Cousins system and to Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) system for late-type giants and vice versa. The giant star sample was formed using surface gravity constraints ({2 log g ≤ 3}) to Cayrel de Strobel et al.' s (2001) spectroscopic catalogueYaz, E. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
82010 -
Transformations between 2MASS, SDSS and BVRI photometric systems: bridging the near-infrared and opticalWe present colour transformations for the conversion of the Two Micron All Sky Survey (2MASS) photometric system to the Johnson-Cousins UBVRI system and further into the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) ugriz system. We have taken SDSS gri magnitudes of stars measured with the 2.5-m telescope from SDSS Data Release 5 (DR5), and BVRI and JHKsBilir, S. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
32008 -
The long Galactic bar as seen by UKIDSS Galactic plane surveyContext: Over the past decade there have been a series of results supporting the hypothesis of the existence of a long thin bar in the Milky Way with a half-length of 4.5 kpc and a position angle of around 45°. This is apparently a very different structure from the triaxial bulge of the Galaxy, which is thicker and shorter and dominates the starCabrera-Lavers, A. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
122008 -
The Distance, Mass, and Radius of the Neutron Star in 4U 1608-52Low-mass X-ray binaries (LMXBs) that show thermonuclear bursts are ideal sources for constraining the equation of state of neutron star matter. The lack of independent distance measurements for most of these sources, however, prevent a systematic exploration of the masses and radii of the neutron stars, hence limiting the equation-of-state studiesGüver, Tolga et al.
Fecha de publicación:
42010 -
SDSS absolute magnitudes for thin-disc stars based on trigonometric parallaxesWe present a new luminosity-colour relation based on trigonometric parallaxes for thin-disc main-sequence stars in Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) photometry. We matched stars from the newly reduced Hipparcos catalogue with the ones taken from Two-Micron All-Sky Survey (2MASS) All-Sky Catalogue of Point Sources, and applied a series of constraintsBilir, S. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
72009 -
Mergers and interactions in Sloan Digital Sky Survey type 2 quasars at z˜ 0.3-0.4. SDSS J143027.66-005614.8: a case studyWe present a compilation of Hubble Space Telescope (HST) images of 58 luminous Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) type 2 active galactic nuclei (AGNs) at ?. Of these, 42 are type 2 quasars, which is a good representation of all optically selected SDSS type 2 quasars in this z range. We find that the majority of the host galaxies are ellipticals (30/42Villar-Martín, M. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
62012 -
Luminosity-colour relations for thin-disc main-sequence starsIn this study we present the absolute magnitude calibrations of thin-disc main-sequence stars in the optical , and in the near-infrared . Thin-disc stars are identified by means of Padova isochrones, and absolute magnitudes for the sample are evaluated via the newly reduced Hipparcos data. The obtained calibrations cover a large range of spectralBilir, S. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
112008 -
Ground-based Multisite Observations of Two Transits of HD 80606bWe present ground-based optical observations of the 2009 September and 2010 January transits of HD 80606b. Based on three partial light curves of the 2009 September event, we derive a midtransit time of Tc [HJD] = 2455099.196 ± 0.026, which is about 1σ away from the previously predicted time. We observed the 2010 January event from nine differentShporer, A. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
102010 -
Probing IGM large-scale flows: warps in galaxies at shells of voidsContext: Hydrodynamical cosmological simulations predict flows of the intergalactic medium along the radial vector of the voids, approximately in the direction of the infall of matter at the early stages of the galaxy formation. Aims: These flows might be detected by analysing the dependence of the warp amplitude on the inclination of the galaxiesLópez-Corredoira, M. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
92008 -
Absence of significant cross-correlation between WMAP and SDSSAims: Several authors have claimed to detect a significant cross-correlation between microwave WMAP anisotropies and the SDSS galaxy distribution. We repeat these analyses to determine the different cross-correlation uncertainties caused by re-sampling errors and field-to-field fluctuations. The first type of error concerns overlapping sky regionsLópez-Corredoira, M. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
42010 -
Detection of transit timing variations in excess of one hour in the Kepler multi-planet candidate system KOI 806 with the GTCAims: We report the detection of transit timing variations (TTVs) well in excess of one hour in the Kepler multi-planet candidate system KOI 806. This system exhibits transits consistent with three separate planets - a Super-Earth, a Jupiter, and a Saturn - lying very nearly in a 1:2:5 resonance, respectively. Methods: We used the Kepler publicTingley, B. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
122011 -
Fossil groups origins. I. RX J105453.3+552102 a very massive and relaxed system at z ~ 0.5Context. The most accepted scenario for the origin of fossil groups is that they are galaxy associations in which the merging rate was fast and efficient. These systems have assembled half of their mass at early epoch of the Universe, subsequently growing by minor mergers, and therefore could contain a fossil record of the galaxy structureAguerri, J. A. L. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
32011 -
Fossil group origins. II. Unveiling the formation of the brightest group galaxies through their scaling relationsContext. Fossil systems are galaxy associations dominated by a relatively isolated, bright elliptical galaxy, surrounded by a group of smaller galaxies lacking L∗ objects. Because of this extreme environment, fossil groups (FGs) are ideal laboratories for studying the mass assembly of brightest group galaxies (BGGs). Aims: We analyzed the nearMéndez-Abreu, J. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
12012