Subvenciones relacionadas:
General
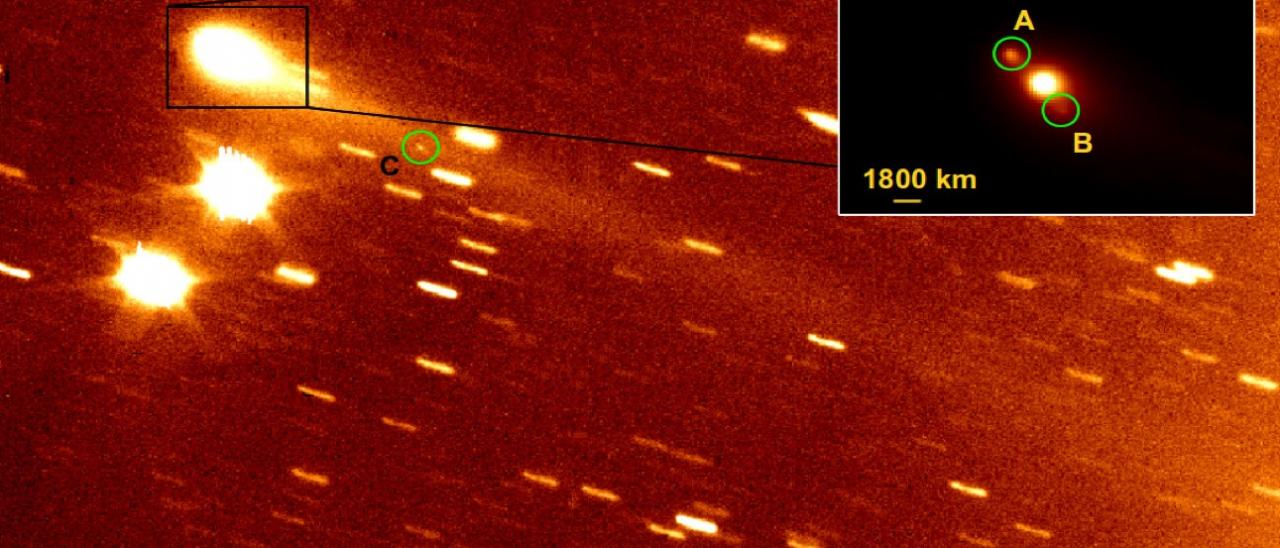
Este Proyecto estudia las propiedades físicas y composicionales de los llamados pequeños cuerpos del Sistema Solar, que incluyen asteroides, objetos helados y cometas. Entre los grupos de mayor interés destacan los objetos trans-neptunianos (TNOs), incluyendo los objetos más lejanos detectados hasta la fecha (Extreme-TNOs o ETNOs); los cometas, y los objetos transicionales cometa-asteroide (Centauros y los llamados Main Belt Comets - MBCs); los asteroides primitivos. Los dos últimos grupos contienen el material más primordial y prístino del Sistema Solar son claves para comprender su origen y evolución. Se destacan entre los asteroides aquellos que se acercan a la órbita de la Tierra (near-Earth asteroids o NEAs), así como los considerados potencialmente peligrosos (Potentially Hazardous Asteroids o PHAs). Debido a su cercanía, los NEAs son los objetos más accesibles al estudio in-situ con misiones espaciales y su futura explotación como fuente de materias primas (asteroid mining). Se destaca el liderazgo por parte del IP del grupo de un survey espectroscópico (visible e infrarrojo cercano) de asteroids primitivos (PRIMitive Asteroid Spectroscopic Survey - PRIMASS). Este proyecto ha recibido financiación de la NASA (17-PDART17_2-0097, IP: N. Pinilla-Alonso, 137.000€ - 2 años) para archivar todos estos espectros (más de 800) en el Small Bodies Node del NASA Planetary Data System.
Los estudios de composición superficial y propiedades físicas y térmicas de estos cuerpos se llevan a cabo utilizando espectroscopia en un amplio rango de longitudes de onda (desde 0.35 a 24 micras), así como imagen y fotometría en el mismo rango. Los datos se interpretan utilizando modelos de scattering y termo-físicos. El proyecto trabaja además en el análisis de las propiedades físicas de los núcleos cometarios y de las propiedades del polvo y el gas en las comas cometarias, muy especialmente en el estudio del polvo en las colas de los MBCs y de los mecanismos por los cuales se emite.
Este grupo mantiene diversas colaboraciones internacionales con otros grupos entre las que podemos destacar: (1) la pertenencia al Grupo de Ciencia de la misión de NASA OSIRIS-REx, en concreto al "Image Processing Working Group", en donde se encarga del tratamiento de los mapas de color que se están obteniendo actualmente con las cámaras OCAMS; (2) la pertenencia al núcleo central de proponentes de las misiones M5 de ESA CASTALIA, CASTAway y Hera; (3) la coordinación de un grupo internacional de estudio de NEAs llamado EURONEAR (European Near Earth Asteroid Research); (4) la pertenencia al "Center for Lunar and Asteroid Surface Science" (CLASS, NASA); (5) la integración en el grupo de Sistema Solar de la misión Euclid; (6) la participación activa en los surveys J-PLUS y J-PASS, en los que trabaja en la explotación de las observaciones de objetos del Sistema Solar; (7) la pertenencia a los grupos de trabajo de Sistema Solar de los telescopios Gaia y JWST.
Miembros
Actividad científica
Publicaciones relacionadas
-
Expected spectral characteristics of (101955) Bennu and (162173) Ryugu, targets of the OSIRIS-REx and Hayabusa2 missionsNASA's OSIRIS-REx and JAXA's Hayabusa2 sample-return missions are currently on their way to encounter primitive near-Earth asteroids (101955) Bennu and (162173) Ryugu, respectively. Spectral and dynamical evidence indicates that these near-Earth asteroids originated in the inner part of the main belt. There are several primitive collisionalde León, J. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
102018 -
PRIMASS visits Hilda and Cybele groupsThe Cybele and Hilda dynamical groups delimit the outer edge of the asteroid belt. Their compositional distribution is a key element to constrain evolutionary models of the Solar System. In this paper, we present a compositional analysis of these populations using spectroscopic observations, SDSS and NEOWISE data. As part of the PRIMASS (PrimitiveDe Prá, M. N. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
92018 -
Visible spectroscopy of the Sulamitis and Clarissa primitive families: a possible link to Erigone and PolanaThe low-inclination (i 8∘) primitive asteroid families in the inner main belt, that is, Polana-Eulalia, Erigone, Sulamitis, and Clarissa, are considered to be the most likely sources of near-Earth asteroids (101955) Bennu and (162173) Ryugu. These two primitive NEAs will be visited by NASA OSIRIS-REx and JAXA Hayabusa 2 missions, respectivelyMorate, D. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
22018 -
New polarimetric and spectroscopic evidence of anomalous enrichment in spinel-bearing calcium-aluminium-rich inclusions among L-type asteroidsAsteroids can be classified into several groups based on their spectral reflectance. Among these groups, the one belonging to the L-class in the taxonomic classification based on visible and near-infrared spectra exhibit several peculiar properties. First, their near-infrared spectrum is characterized by a strong absorption band interpreted as theDevogèle, M. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
42018 -
Visible spectra of (474640) 2004 VN112-2013 RF98 with OSIRIS at the 10.4 m GTC: evidence for binary dissociation near aphelion among the extreme trans-Neptunian objectsThe existence of significant anisotropies in the distributions of the directions of perihelia and orbital poles of the known extreme trans-Neptunian objects (ETNOs) has been used to claim that trans-Plutonian planets may exist. Among the known ETNOs, the pair (474640) 2004 VN112-2013 RF98 stands out. Their orbital poles and the directions of theirde León, J. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
52017 -
280 one-opposition near-Earth asteroids recovered by the EURONEAR with the Isaac Newton TelescopeContext. One-opposition near-Earth asteroids (NEAs) are growing in number, and they must be recovered to prevent loss and mismatch risk, and to improve their orbits, as they are likely to be too faint for detection in shallow surveys at future apparitions. Aims: We aimed to recover more than half of the one-opposition NEAs recommended forVaduvescu, O. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
12018 -
Disrupted Asteroid P/2016 G1. II. Follow-up Observations from the Hubble Space TelescopeAfter the early observations of the disrupted asteroid P/2016 G1 with the 10.4 m Gran Telescopio Canarias (GTC) and modeling of the dust ejecta, we have performed a follow-up observational campaign of this object using the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) during two epochs (2016 June 28 and July 11). The analysis of these HST images with the same modelMoreno, F. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
122017 -
The EURONEAR Lightcurve Survey of Near Earth AsteroidsThis data paper presents lightcurves of 101 near Earth asteroids (NEAs) observed mostly between 2014 and 2017 as part of the EURONEAR photometric survey using 11 telescopes with diameters between 0.4 and 4.2 m located in Spain, Chile, Slovakia and Romania. Most targets had no published data at the time of observing, but some objects were observedVaduvescu, O. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
82017 -
Physical and dynamical properties of the anomalous comet 249P/LINEARImages and low-resolution spectra of the near-Earth Jupiter family comet (JFC) 249P/LINEAR in the visible range obtained with the instrument OSIRIS in the 10.4 m Gran Telescopio Canarias (GTC) (La Palma, Spain) on January 3, 4, 6 and February 6, 2016 are presented, together with a series of images obtained with the 0.4m telescope of the GreatFernández, Julio A. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
102017 -
Meteor studies in the framework of the JEM-EUSO programWe summarize the state of the art of a program of UV observations from space of meteor phenomena, a secondary objective of the JEM-EUSO international collaboration. Our preliminary analysis indicates that JEM-EUSO, taking advantage of its large FOV and good sensitivity, should be able to detect meteors down to absolute magnitude close to 7. ThisAbdellaoui, G. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
92017 -
V-type candidates and Vesta family asteroids in the Moving Objects VISTA (MOVIS) catalogueContext. Basaltic asteroids (spectrally classified as V-types) are believed to be fragments of large differentiated bodies. The majority of them are found in the inner part of the asteroid belt, and are current or past members of the Vesta family. Recently, some V-type asteroids have been discovered far from the Vesta family supporting theLicandro, J. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
42017 -
The 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko observation campaign in support of the Rosetta missionWe present a summary of the campaign of remote observations that supported the European Space Agency's Rosetta mission. Telescopes across the globe (and in space) followed comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko from before Rosetta's arrival until nearly the end of the mission in September 2016. These provided essential data for mission planning, largeSnodgrass, C. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
52017 -
Non-Vestoid candidate asteroids in the inner main beltContext. Most howardite-eucrite-diogenite (HED) meteorites (analogues to V-type asteroids) are thought to originate from the asteroid (4) Vesta. However some HEDs show distinct oxygen isotope ratios and therefore are thought to originate from other asteroids. In this study we try to identify asteroids that may represent parent bodies of thoseOszkiewicz, D. A. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
32017 -
The Splitting of Double-component Active Asteroid P/2016 J1 (PANSTARRS)We present deep imaging observations, orbital dynamics, and dust-tail model analyses of the double-component asteroid P/2016 J1 (J1-A and J1-B). The observations were acquired at the Gran Telescopio Canarias (GTC) and the Canada–France–Hawaii Telescope (CFHT) from mid-March to late July of 2016. A statistical analysis of backward-in-timeMoreno, F. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
32017 -
The Remote Observatories of the Southeastern Association for Research in Astronomy (SARA)We describe the remote facilities operated by the Southeastern Association for Research in Astronomy (SARA) , a consortium of colleges and universities in the US partnered with Lowell Observatory, the Chilean National Telescope Allocation Committee, and the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias. SARA observatories comprise a 0.96 m telescope at KittKeel, W. C. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
12017 -
The JEM-EUSO mission: An introductionThe Extreme Universe Space Observatory on board the Japanese Experiment Module of the International Space Station, JEM-EUSO, is being designed to search from space ultra-high energy cosmic rays. These are charged particles with energies from a few 1019 eV to beyond 1020 eV, at the very end of the known cosmic ray energy spectrum. JEM-EUSO will alsoAdams, J. H. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
112015 -
The JEM-EUSO instrumentIn this paper we describe the main characteristics of the JEM-EUSO instrument. The Extreme Universe Space Observatory on the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM-EUSO) of the International Space Station (ISS) will observe Ultra High-Energy Cosmic Rays (UHECR) from space. It will detect UV-light of Extensive Air Showers (EAS) produced by UHECRsAdams, J. H. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
112015 -
The atmospheric monitoring system of the JEM-EUSO instrumentThe JEM-EUSO telescope will detect Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Rays (UHECRs) from space, detecting the UV Fluorescence Light produced by Extensive Air Showers (EAS) induced by the interaction of the cosmic rays with the earth's atmosphere. The capability to reconstruct the properties of the primary cosmic ray depends on the accurate measurement of theAdams, J. H. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
112015 -
The infrared camera onboard JEM-EUSOThe Extreme Universe Space Observatory on the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM-EUSO) on board the International Space Station (ISS) is the first space-based mission worldwide in the field of Ultra High-Energy Cosmic Rays (UHECR). For UHECR experiments, the atmosphere is not only the showering calorimeter for the primary cosmic rays, it is anAdams, J. H. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
112015 -
Calibration aspects of the JEM-EUSO missionThe JEM-EUSO telescope will be, after calibration, a very accurate instrument which yields the number of received photons from the number of measured photo-electrons. The project is in phase A (demonstration of the concept) including already operating prototype instruments, i.e. many parts of the instrument have been constructed and testedAdams, J. H. et al.
Fecha de publicación:
112015