Subvenciones relacionadas:
General
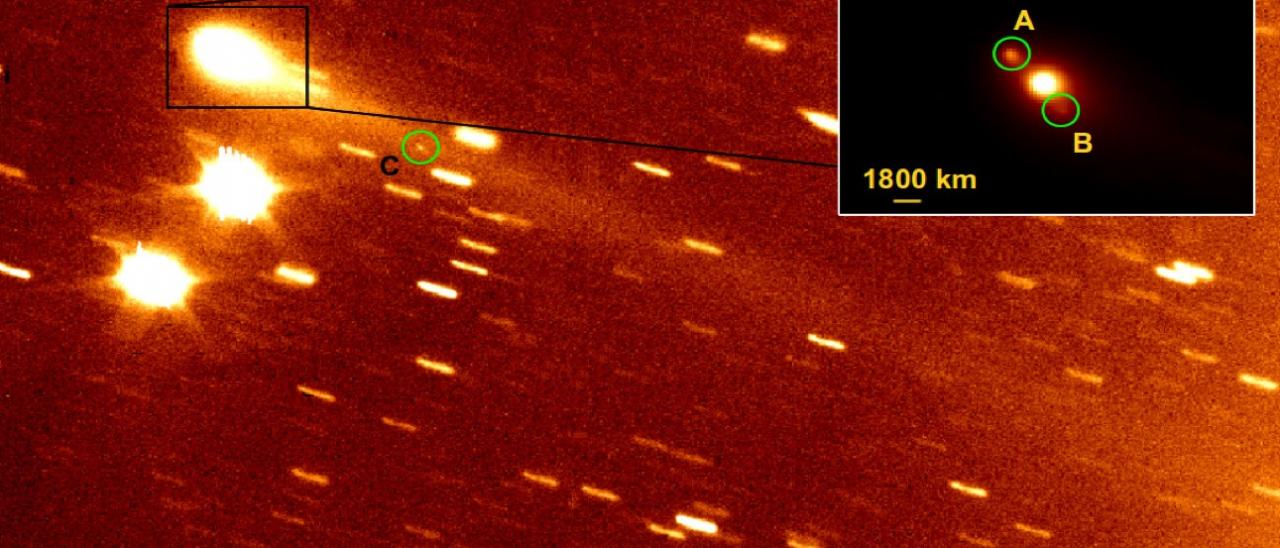
Este Proyecto estudia las propiedades físicas y composicionales de los llamados pequeños cuerpos del Sistema Solar, que incluyen asteroides, objetos helados y cometas. Entre los grupos de mayor interés destacan los objetos trans-neptunianos (TNOs), incluyendo los objetos más lejanos detectados hasta la fecha (Extreme-TNOs o ETNOs); los cometas, y los objetos transicionales cometa-asteroide (Centauros y los llamados Main Belt Comets - MBCs); los asteroides primitivos. Los dos últimos grupos contienen el material más primordial y prístino del Sistema Solar son claves para comprender su origen y evolución. Se destacan entre los asteroides aquellos que se acercan a la órbita de la Tierra (near-Earth asteroids o NEAs), así como los considerados potencialmente peligrosos (Potentially Hazardous Asteroids o PHAs). Debido a su cercanía, los NEAs son los objetos más accesibles al estudio in-situ con misiones espaciales y su futura explotación como fuente de materias primas (asteroid mining). Se destaca el liderazgo por parte del IP del grupo de un survey espectroscópico (visible e infrarrojo cercano) de asteroids primitivos (PRIMitive Asteroid Spectroscopic Survey - PRIMASS). Este proyecto ha recibido financiación de la NASA (17-PDART17_2-0097, IP: N. Pinilla-Alonso, 137.000€ - 2 años) para archivar todos estos espectros (más de 800) en el Small Bodies Node del NASA Planetary Data System.
Los estudios de composición superficial y propiedades físicas y térmicas de estos cuerpos se llevan a cabo utilizando espectroscopia en un amplio rango de longitudes de onda (desde 0.35 a 24 micras), así como imagen y fotometría en el mismo rango. Los datos se interpretan utilizando modelos de scattering y termo-físicos. El proyecto trabaja además en el análisis de las propiedades físicas de los núcleos cometarios y de las propiedades del polvo y el gas en las comas cometarias, muy especialmente en el estudio del polvo en las colas de los MBCs y de los mecanismos por los cuales se emite.
Este grupo mantiene diversas colaboraciones internacionales con otros grupos entre las que podemos destacar: (1) la pertenencia al Grupo de Ciencia de la misión de NASA OSIRIS-REx, en concreto al "Image Processing Working Group", en donde se encarga del tratamiento de los mapas de color que se están obteniendo actualmente con las cámaras OCAMS; (2) la pertenencia al núcleo central de proponentes de las misiones M5 de ESA CASTALIA, CASTAway y Hera; (3) la coordinación de un grupo internacional de estudio de NEAs llamado EURONEAR (European Near Earth Asteroid Research); (4) la pertenencia al "Center for Lunar and Asteroid Surface Science" (CLASS, NASA); (5) la integración en el grupo de Sistema Solar de la misión Euclid; (6) la participación activa en los surveys J-PLUS y J-PASS, en los que trabaja en la explotación de las observaciones de objetos del Sistema Solar; (7) la pertenencia a los grupos de trabajo de Sistema Solar de los telescopios Gaia y JWST.