Subvenciones relacionadas:
General
Los agujeros negros y estrellas de neutrones en binarias de rayos-X son laboratorios únicos para explorar la física de estos objetos compactos. No solo permiten confirmar la existencia de agujeros negros de origen estelar a través de mediciones dinámicas de sus masas, sino que también permiten investigar el comportamiento de la materia y la radiación bajo la influencia de un campo gravitatorio extremo. De este modo, es posible estudiar la física del proceso de acreción, la forma más eficiente de producción de energía conocida. El conocimiento de este proceso es esencial para entender el Universo, jugando un papel crucial en la astronomía galáctica y extra-galáctica.
Los objetivos científicos que se persiguen son:
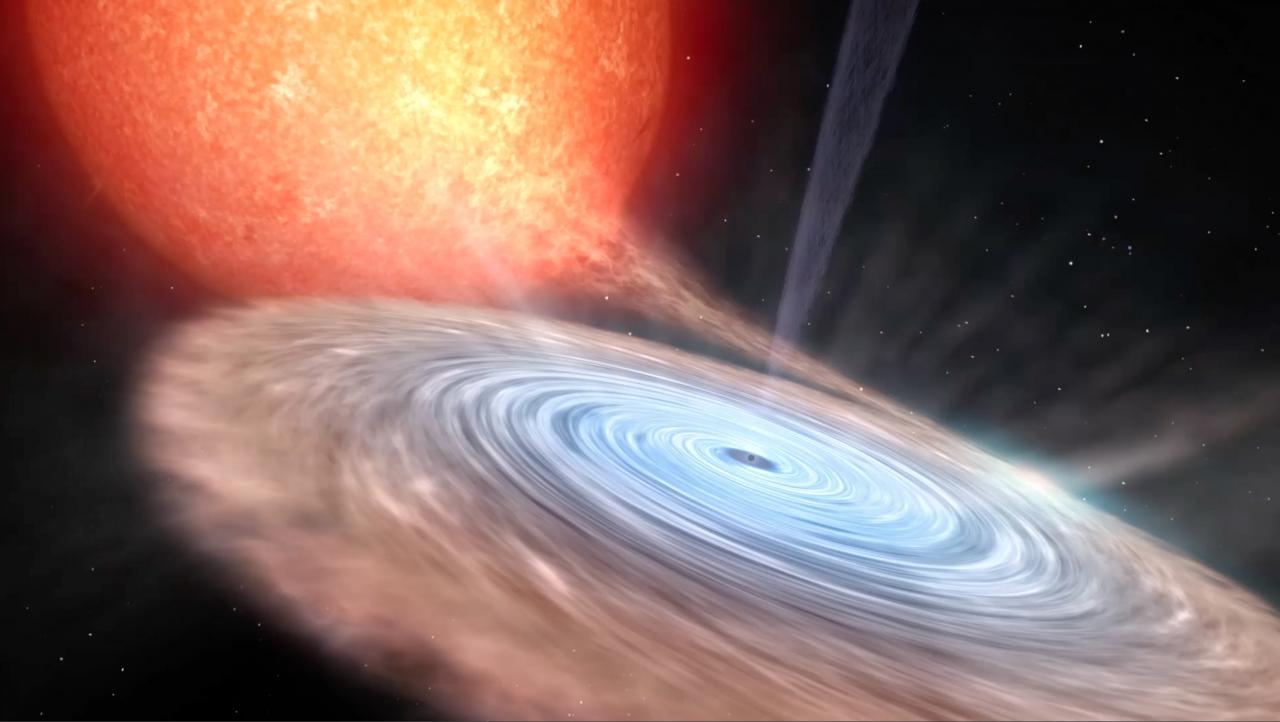
- Estudios de acreción y eyección. Esta línea explota una fenomenología que nuestro grupo ha descubierto recientemente y se enfoca en la relación universal existente entre el proceso de acreción en agujeros negros y los procesos de expulsión en forma de jets colimados y vientos. Se pondrá énfasis en las propiedades generales y el efecto que el viento frío que hemos descubierto en binarias de rayos-X tiene sobre todo el proceso de acreción. Investigaremos como de comunes son estos vientos, como afectan al proceso de acrecimiento en el agujero negro y cuál es su relación con los jets y los vientos observados en rayos-X. Asimismo se realizarán estudios espectrales detallados en rayos X, con el fin de caracterizar los diferentes estados y geometrías de acreción en función de la luminosidad.
- Tenemos como objetivo definir la distribución de masas de agujeros negros estelares y estrellas de neutrones. Para ello medimos masas en binarias de rayos-X, continuando así nuestra ya reconocida contribución a uno de los experimentos fundamentales en la astrofísica moderna. De este modo, esperamos mejorar significativamente las distribuciones conocidas de objetos compactos, lo cual permitirá verificar modelos de explosión de supernovas y evolución de binarias compactas; además de obtener límites a la ecuación de estado de la materia nuclear. Para ello, mediremos las masas en binarias de rayos-X conocidas o recientemente descubiertas, e intentaremos encontrar un gran número de nuevas binarias de rayos X en nuestra galaxia que puedan después ser estudiadas dinámicamente.
- Analizar la estructura y variabilidad de los discos de acreción alrededor de los objetos compactos en diferentes bandas espectrales (óptico-rayos X). La distribución espectral durante la erupción (especialmente a altas energías) y su variación temporal es esencial para restringir los modelos de erupción y la estructura física del disco (e.g. radio del disco advectivo) así como la contribución del jet a la emisión en el visible y el infrarrojo.
Miembros
Resultados
- Nuestro equipo ha liderado un ambicioso estudio multi-frecuencia que cubrió las dos erupciones de 2015 del agujero negro transitorio V404 Cyg. Este evento ha sido uno de los más interesantes jamás observados de este tipo. En 2018 publicamos el trabajo global que recoge todos los datos espectroscópicos tomados en 1989 y 2015.
- Presentamos la evidencia de viento similar al detectado en V404 Cyg en un segundo sistema con agujero negro, V4641 Sgr.
- Se publicó tanto el artículo final como un estudio piloto sobre el método desarrollado por el grupo para descubrir y medir masas en agujeros negros en quietud. Esta técnica, potencialmente, podría triplicar la población conocida de estos objetos.
- Se medió la masa de la estrella de neutrones en PSR J2215+5135, una de las más masivas que se conocen hasta la fecha.
- Se presentó el primer estudio detallado del sistema ultra-compacto SLX 1737-282.