Subvenciones relacionadas:
General
El objetivo general del Proyecto es el estudio de la estructura, historia evolutiva y proceso de formación de galaxias a través de sus poblaciones estelares resueltas, tanto a partir de fotometría como espectroscopia. El proyecto puede dividirse en cuatro líneas principales:
I. Historia de formación estelar en el Grupo Local.
El objetivo de esta línea es la caracterización de la estructura espacio-temporal de las galaxias del Grupo Local mediante la observación de sus estrellas individuales. Un objetivo fundamental es la determinación de las historias de la formación estelar (HFE) detalladas y extendidas a toda la historia evolutiva de la galaxia con objeto de determinar el grado de importancia que los procesos cosmológicos (tales como la reionización o self-shielding) o locales (barrido de gas por supernovas, fuerzas de marea, migración estelar) tuvieron en su formación.
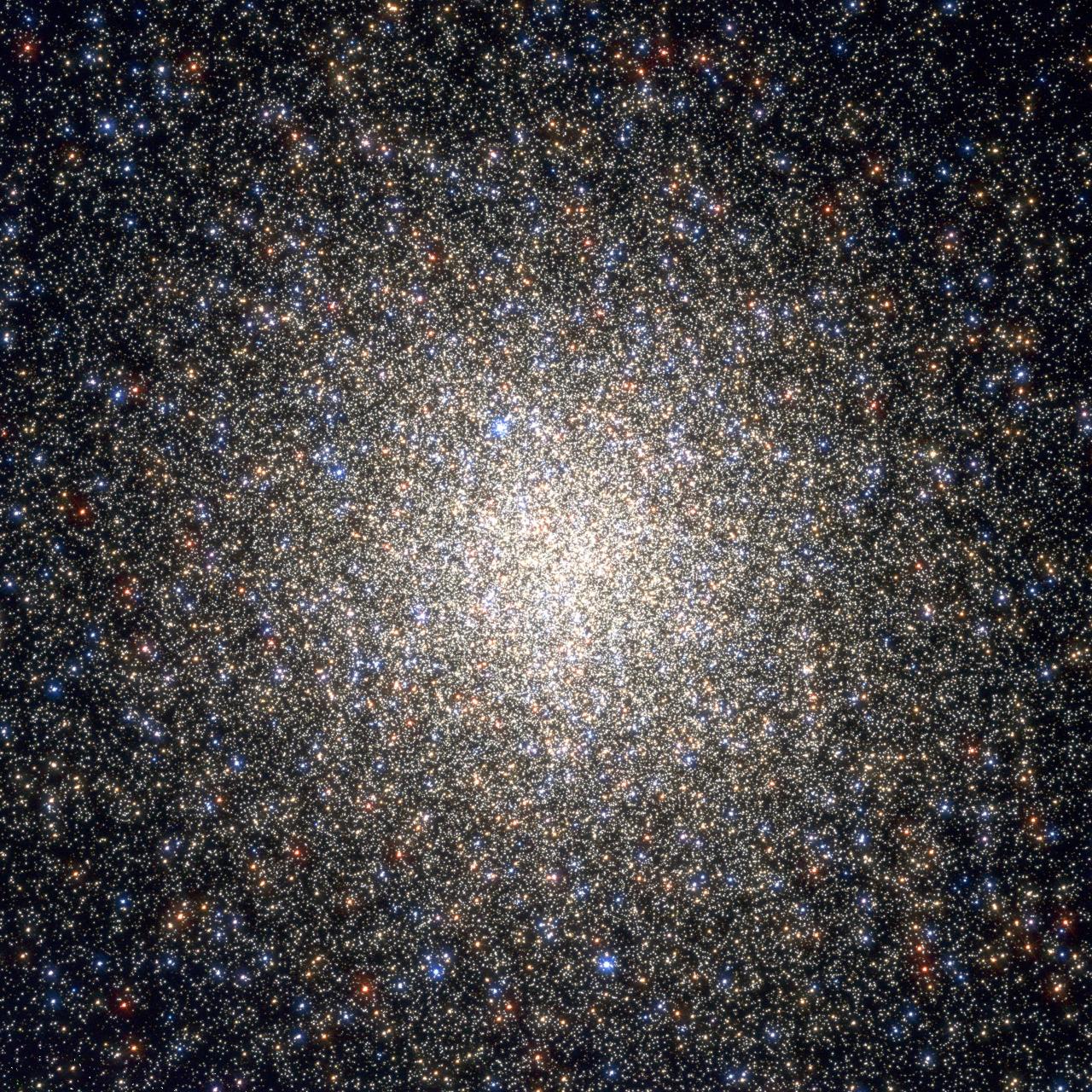
II. Multipoblaciones estelares en cúmulos globulares.
De forma contraria al paradigma clásico, hay evidencias de que los cúmulos globulares (CG) albergan más de una población estelar de diferente composición química. Observaciones fotométricas de los CG usando el HST muestran fuertes evidencias de múltiples secuencias principales en el DCM. El objetivo de la línea es caracterizar dichas multipoblaciones en CG.
III. Formación y estructura de la Vía Láctea.
Esta línea tiene como eje principal el estudio de la Vía Láctea a través de los datos que proporcionará GAIA (espacio) y el survey ESO-VVV . Este tipo de datos van a dar una oportunidad única de conocer la historia de formación estelar en el disco y en el bulbo galáctico. En este marco, es necesario adecuar las herramientas desarrolladas por nuestro grupo para el análisis de poblaciones estelares al tipo de datos que está suministrando ambos surveys.
IV. Evolución estelar y diagrama color-magnitud sintético.
Nuestro grupo ha liderado el desarrollo de una nueva librería de evolución estelar. Hay una necesidad en la comunidad científica de mejorar la confianza y exactitud de la computación de modelos estelares mediante la incorporación de las últimas mejoras en el campo de la física tales como la Ecuación de Estado, nuevos cálculos en tablas de opacidades o en secciones nucleares effectivas.
Miembros
Resultados
- Desarrollo de la web http://basti-iac.oa-teramo.inaf.it de la librería BaSTI
- Obtención de fotometría PSF en el IR próximo de la región completa del disco galáctico procedente de VVV (220 grados cuadrados entre 294.7° ≤ l ≤ 350.0° y |b| ≤ 2.25°) en J y K
- Elaboración de una base de datos completa de "mapas cromosómicos", de acceso público, para todos los objetos del "HST Legacy Project on Globular Clusters".
- Determinación de las Historias de Formación Estelar de tres galaxias ultra-débiles (UFD): Bootes I, Canes Venatici II y Leo IV